The European job market in 2024 is complex. It faces economic challenges and opportunities. Unemployment rates show big differences across the continent.
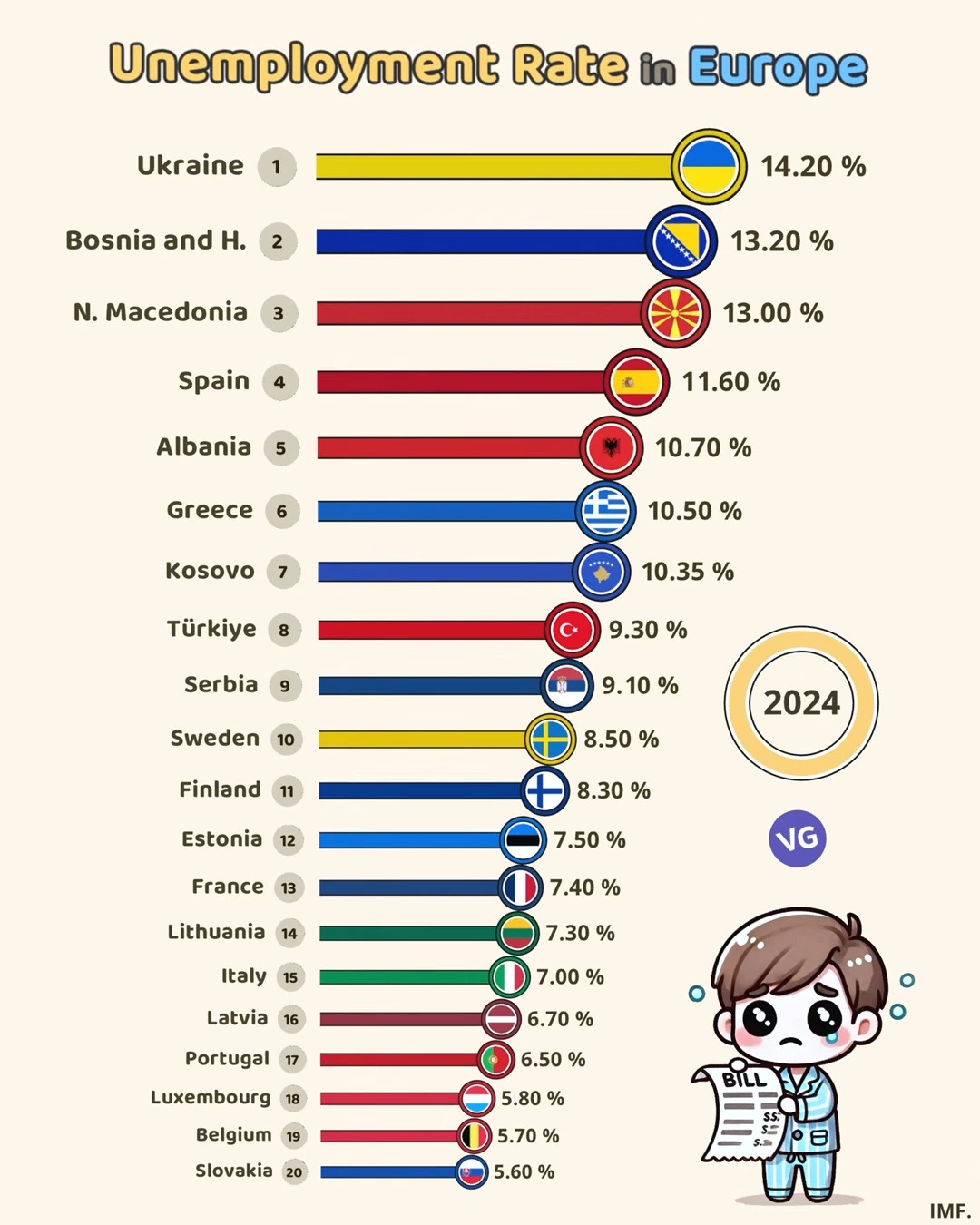
Unemployment Rate in Europe 2024
| Rank | Country | Flag | Unemployment Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ukraine | 🇺🇦 | 14.20 |
| 2 | Bosnia and H. | 🇧🇦 | 13.20 |
| 3 | N. Macedonia | 🇲🇰 | 13.00 |
| 4 | Spain | 🇪🇸 | 11.60 |
| 5 | Albania | 🇦🇱 | 10.70 |
| 6 | Greece | 🇬🇷 | 10.50 |
| 7 | Kosovo | 🇽🇰 | 10.35 |
| 8 | Türkiye | 🇹🇷 | 9.30 |
| 9 | Serbia | 🇷🇸 | 9.10 |
| 10 | Sweden | 🇸🇪 | 8.50 |
| 11 | Finland | 🇫🇮 | 8.30 |
| 12 | Estonia | 🇪🇪 | 7.50 |
| 13 | France | 🇫🇷 | 7.40 |
| 14 | Lithuania | 🇱🇹 | 7.30 |
| 15 | Italy | 🇮🇹 | 7.00 |
| 16 | Latvia | 🇱🇻 | 6.70 |
| 17 | Portugal | 🇵🇹 | 6.50 |
| 18 | Luxembourg | 🇱🇺 | 5.80 |
| 19 | Belgium | 🇧🇪 | 5.70 |
| 20 | Slovakia | 🇸🇰 | 5.60 |
This analysis looks at unemployment in Europe. It finds key trends and solutions for the future.
The Current State of European Unemployment
The European job market is very different today. Unemployment rates vary from 5.6% to 14.2%. This shows big differences in economic strength and job market flexibility.
Regional job trends are also different. Nordic countries have stable jobs, while Southern and Eastern Europe struggle. These differences come from economic diversity and job market adaptability.
Key economic signs show how healthy the job market is. GDP growth, inflation, and job participation rates vary by region. This shows how economic growth affects jobs differently in each place.
Top 5 Countries Facing Employment Challenges
Ukraine has the highest unemployment rate at 14.2%. Bosnia and Herzegovina and North Macedonia follow with rates of 13.2% and 13%. Spain and Albania have rates of 11.6% and 10.7% respectively. These numbers show both long-term and short-term job market issues.
Critical Analysis of Most Affected Nations
Ukraine’s job crisis comes from war and economic changes. The conflict has hurt businesses and changed the job market. Industrial areas face big challenges.
The Balkans struggle with job markets due to structural problems. Bosnia and Herzegovina and North Macedonia lack economic diversity and modern industries. Demographic issues and limited regional integration make things worse.
Spain’s youth job crisis is severe. Despite being a big economy, it has a dual job market that hurts young people. Temporary and seasonal jobs create job uncertainty for the young.
Factors Driving High Unemployment
Recovering from the pandemic is hard for European jobs. COVID-19 has changed some sectors forever. The tourism and hospitality industries in Southern Europe are still adjusting.
Job market problems exist in many ways. Strict job laws, high costs, and limited job movement make it hard to find work. These issues are worse in countries with strict job rules.
There’s a big gap between job skills and what employers want. New technologies have made some jobs obsolete. Places with little training face big challenges in keeping up.
Digital changes are changing jobs. Automation and AI are making some jobs disappear but creating new ones. Places without good digital skills and training struggle to adapt.
Comparative Analysis with Lower Unemployment Nations
Countries with lower unemployment rates have some common traits. Latvia, Portugal, Luxembourg, Belgium, and Slovakia have done well with job policies and economic diversity.
These countries have good vocational training, flexible job laws, and strong partnerships. Their success can help other countries with high unemployment.
These countries’ education systems match job needs well. They offer training that leads to jobs and help workers keep up with new demands.
Solutions and Future Outlook
The European Union has started many programs to help with joblessness. The NextGenerationEU and regional funds are big steps towards creating jobs and improving skills.
Digital skills are key in today’s job market. Countries are focusing on teaching these skills through new programs. They aim to prepare workers for the future.
Switching to new industries can help fight joblessness. Places moving from old to new economies are more stable. They can better handle job changes and economic ups and downs.
By 2025, jobs will likely shift more towards digital and green fields. There will be more demand for skills in clean energy and digital services. But, this change might make it harder for some areas to find jobs.
Policy Recommendations
For now, we need to create jobs and improve skills quickly. Wage subsidies, job-sharing, and temporary jobs can help during tough times.
For the long run, we need to change how we work and protect jobs. We should update job laws, improve job training, and make education more relevant to work.
Working together across borders can help solve job problems. Sharing training, moving workers, and planning economies together can balance job markets in Europe.
We need new ways to create jobs. Things like remote work, flexible jobs, and new business ideas can help lower joblessness.
Impact on Social and Economic Development
People moving to other places shows job problems in Europe. Places with few jobs lose young, skilled workers. This makes things worse for those places.
Long joblessness puts pressure on social security. It costs more money and hurts the system. This makes it hard to keep social safety nets strong.
Joblessness affects more than just jobs. It means less spending, less money for the government, and slower growth. These problems make it hard to get back on track.
Unemployment also hurts communities and health. It makes it harder for people to move up in life. Fixing joblessness is key to keeping society stable and fair.
In summary, solving joblessness in Europe needs a mix of quick fixes and long-term changes. Success stories show the value of flexible work, good education, and creative job policies. As Europe faces new challenges, it’s important to keep working on job disparities for growth and fairness.