Did you know the United States only made 12,000 tons of olive oil in the 2023/24 crop year? This is according to the United States Department of Agriculture1. But, the real giant in olive oil production is Spain, making over 50% of the world’s olive oil2.
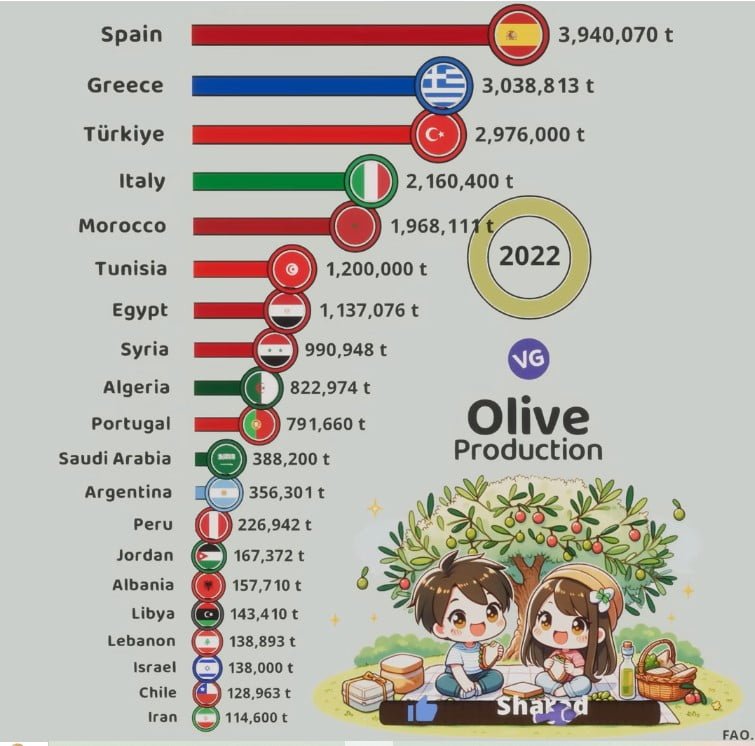
| Rank | Country | Flag | Production (tonnes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Spain | 🇪🇸 | 3,940,070 |
| 2 | Greece | 🇬🇷 | 3,038,813 |
| 3 | Türkiye | 🇹🇷 | 2,976,000 |
| 4 | Italy | 🇮🇹 | 2,160,400 |
| 5 | Morocco | 🇲🇦 | 1,968,111 |
| 6 | Tunisia | 🇹🇳 | 1,200,000 |
| 7 | Egypt | 🇪🇬 | 1,137,076 |
| 8 | Syria | 🇸🇾 | 990,948 |
| 9 | Algeria | 🇩🇿 | 822,974 |
| 10 | Portugal | 🇵🇹 | 791,660 |
| 11 | Saudi Arabia | 🇸🇦 | 388,200 |
| 12 | Argentina | 🇦🇷 | 356,301 |
| 13 | Peru | 🇵🇪 | 226,942 |
| 14 | Jordan | 🇯🇴 | 167,372 |
| 15 | Albania | 🇦🇱 | 157,710 |
| 16 | Libya | 🇱🇾 | 143,410 |
| 17 | Lebanon | 🇱🇧 | 138,893 |
| 18 | Israel | 🇮🇱 | 138,000 |
| 19 | Chile | 🇨🇱 | 128,963 |
| 20 | Iran | 🇮🇷 | 114,600 |
Spain stands out in the olive oil world, with key areas like Andalusia, Catalonia, and Jaén leading the way2. The United States is growing, but it still lags behind the top producers. Despite this, California-based producers shone at the prestigious NYIOOC competition, winning 86 out of 95 awards1.
Key Takeaways
- Spain is the world’s largest producer of olive oil, accounting for over 50% of global production2.
- The United States produced only 12,000 tons of olive oil in the 2023/24 crop year, a far cry from global leaders like Spain1.
- American producers are gaining recognition, with California-based producers earning 86 out of 95 awards at the NYIOOC competition1.
- The main olive oil-producing regions in Spain include Andalusia, Catalonia, and Jaén2.
- The United States has yet to challenge the global leaders in olive oil production, despite its growing industry1.
Introduction to Olive Oil Production
Olive Production by Country (2022)
Source: FAO
The story of olive oil goes way back, thousands of years. It started in ancient Persia, Mesopotamia, and the Mediterranean3. People first made olive oil in Galilee around 6000 BC. By 4500 BC, a settlement near Haifa was already making olive oil3. In Crete, olive trees became a big deal in the economy after a certain period.
Origins and History of Olive Cultivation
The olive tree and its olive oil have been key to Mediterranean cuisine for ages. By 2400 BC, olive oil was big in the city-state of Ebla near Aleppo3. Before 2000 BC, Egypt was getting olive oil from Crete, Syria, and Canaan. They found jugs over 4,000 years old3. Olive oil was a big deal in Mycenaean Greece around 1450-1150 BC3.
Importance of Olive Oil in Mediterranean Cuisine
Olive oil has been used for many things, like cooking, religious rituals, medicine, and skincare3. By the 1st century AD, Italy was known for its great olive oil, as Pliny the Elder said3. Joseph Graham made a big change in 1795 with the hydraulic pressing system, making olive oil production better3.
“Olive oil has been a staple of Mediterranean cuisine for centuries, forming one of the three core food plants in the region, along with wheat and grapes.”
Spain: The Undisputed Leader
Spain leads the world in olive oil production, making up about 45% of it4. Its climate, large olive tree farms, and advanced methods make it a top producer. This has made Spain the leader in olive oil.
Andalucia in the south is where most of Spain’s olive oil comes from, producing half of the country’s oil4. The Priego de Cordoba olive oil is the top award-winning type worldwide4. It celebrated 20 years in 2015, with its oils winning top spots in competitions4.
Factors Contributing to Spain’s Dominance
Several factors make Spain a leader in olive oil:
- Spain’s climate is perfect for olive trees, thanks to its warmth and dryness4.
- It has the most olive trees in the world, covering a vast area5.
- Producers use modern tech and sustainable farming for quality oil5.
- Spain has strong trade links in Europe and worldwide to sell its olive oil4.
When buying extra virgin olive oil, check for harvest dates, producer names, and where it was made4.
“Seven out of the top 10 best olive oils in the world come from Spain, with only one from Italy.”4
Spain’s olive oil history is deep, with records showing it sent a lot of oil to Italy in Roman times465.
Italy: A Prominent Producer
While Spain leads in Italy olive oil production, Italy is a key player, often ranking second globally. It boasts a long history of making olive oil. This has made it a major exporter of top-quality olive oils for centuries. The Italian olive oil industry boosts the economy and culture of the country.
In 2019, Italy shipped out 338 thousand tons of olive oil, making it a top exporter7. Most of this, 82%, comes from Southern Italy. Puglia and Calabria lead with 68% of the total7. Other regions like Sicilia, Campania, Abruzzo, Lazio, Toscana, and Umbria also play a part7.
Italy is a big name in olive oil production, accounting for 25-30% of the world’s output8. A bottle of high-quality extra virgin olive oil from Italy can cost between $15 to $607. The quality levels range from extra virgin to lampante, with extra virgin being the top grade7.
Italian producers won 97 Gold and 50 Silver Awards at the 2024 NYIOOC World Olive Oil Competition9. This shows the high quality and tradition of Italy’s olive oil.
Tuscany might be famous, but it only makes 2% to 3% of Italy’s olive oil7. Olive oil companies often claim their oil is the best, adding to the competition7. This competition makes each olive oil unique for different dishes or cooking methods7. Making olive oil is hard work because it takes a long time for olive trees to produce and the process is complex7.
“The unique Casaliva cultivar played a significant role in the success of Uliva, along with the efforts of around 1,200 local producers.”
As Italy keeps innovating, its olive oil industry remains a source of pride. It showcases the lasting impact of Mediterranean culinary traditions978.
Greece: Steeped in Olive Heritage
Greece has a long history with Greece olive oil, dating back thousands of years. Olive trees and oil are key parts of Greek culture. They symbolize peace and are used in many ways, from cooking to religious rituals. Greece is a top producer of Greece olive oil, and its people love it, showing its cultural significance in Greece.
High Consumption and Cultural Significance
Greece loves Greece olive oil a lot. It has about 127 million olive trees for oil and 37 million for table olives10. This makes olive oil a big part of Greek life and food.
Greece olive oil is more than just food. It’s a symbol of peace and prosperity. The olive tree is seen as a gift from the goddess Athena, adding to its importance.
People in Greece value Greece olive oil for more than just cooking. Studies show it’s good for your health10. The Mediterranean diet, with olive oil at its core, is known for its health benefits10.
Greece’s Greece olive oil is celebrated worldwide. In the 2024 NYIOOC World Olive Oil Competition, Greek oils won 56 awards11. This proves the quality and tradition of Greek olive oil makers.
Greece olive oil is a big part of Greek culture and identity. Its long history and ongoing popularity show the lasting impact of olive oil on Greece121011.
biggest producer of olive oil in the world
Spain leads the world in olive oil production, making over 40% of the global supply13. Its success comes from a great Mediterranean climate, widespread olive trees, top-notch production methods, and strong trade ties3. Spain produces about 63% of the EU’s olive oil, making it a giant in the global market14.
Italy is the second-biggest producer, adding 10% to the world’s olive oil13. Countries like Greece, Portugal, Tunisia, Turkey, and Morocco also produce olive oil, but Spain is far ahead3.
Olive oil production has doubled in 30 years, with the Mediterranean making 80% of it13. But, production levels have varied over the years13. New players like Algeria, Argentina, Chile, the U.S., Australia, Egypt, and China are entering the scene, but they’re still small compared to the big names13.
Olive oil has been key in Mediterranean cooking since ancient times, starting in the 8th millennium BC3. Its value soared after the Romans conquered Egypt, Greece, and Asia Minor3.
“Olive oil has been a common ingredient in Mediterranean cuisine since ancient times, including in ancient Greek and Roman cuisine.”3
Spain’s success in olive oil comes from its long history, great climate, and advanced farming13143. As the top producer, Spain greatly influences the global olive oil market and meets the increasing demand for this tasty food staple13143.
Top Olive Oil Producing Countries
The world’s olive oil comes mainly from a few top producers. Spain leads, making nearly half of the world’s olive oil3. Italy, Greece, Portugal, Tunisia, Turkey, and Morocco are also big producers.
Olive oil quality is key, with strict standards for the best extra virgin oil3. To be top quality, it can’t have more than 0.8% free acidity3. Olive oil is mostly oleic acid, with smaller amounts of other acids.
Production Statistics and Trends
Olive oil has a long history, dating back to the 8th millennium BC3. Ancient Greeks and Romans used it a lot in cooking. Mycenaean Greece even traded it around 1450-1150 BC3.
2 Spain leads in olive oil production, followed by Italy and Greece2. Each country has its own olive types, like Picual in Spain and Koroneiki in Greece, each with unique tastes2.
2 Spanish and Italian olive oils are known for their quality, often with special designations2. Greek producers stick to traditional ways, like hand-picking and cold pressing2.
2 Spain and Italy use new tech to make their olive oil better, but Greece keeps it traditional2. All three countries have special olive oils with Protected Designation of Origin (PDO), showing their unique olive oil culture.
“Olive oil has been a cornerstone of Mediterranean cuisine and culture for millennia, deeply rooted in the history and traditions of the region.”
Olive Oil Quality and Varieties
Olive oil is a versatile and highly prized culinary ingredient. It comes in many qualities and varieties for different tastes and uses. From the golden extra virgin olive oil to the delicate refined types, the world of olive oil is vast15.
Factors Affecting Olive Oil Quality
The quality of olive oil depends on several factors. These include the type of olive, the altitude, when it’s harvested, and how it’s made15. Extra virgin olive oil is the top quality, with less than 0.8% acidity. It has a fruity and strong taste15. Other types, like virgin, refined, and pomace olive oil, have their own special qualities for different cooking needs.
The ripeness of the olives, how they’re processed, and how they’re stored affect the oil’s quality15. Keeping the oil handled and stored right is key to keeping its flavors and health benefits. This makes olive oil a favorite in kitchens worldwide.
| Olive Oil Variety | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Extra Virgin Olive Oil | – Highest quality with free acidity ≤ 0.8% – Robust, fruity, and pungent flavor – Minimally processed, retaining more nutrients |
| Virgin Olive Oil | – Good quality with free acidity ≤ 2% – Mild, fruity flavor – Slightly more processed than extra virgin |
| Refined Olive Oil | – Mild, neutral flavor – Lower quality with free acidity ≤ 0.3% – Produced through chemical refining process |
| Pomace Olive Oil | – Obtained from olive pomace (leftover solids) – Neutral flavor, suitable for high-heat cooking – Lower quality with free acidity ≤ 0.3% |
Knowing about olive oil quality and varieties is key for those who love food and cooking15. By understanding what makes olive oil special, we can explore new flavors and use it better in our cooking.
“The quality of olive oil is a reflection of the care and attention given to every step of its production, from the cultivation of the olives to the final bottling.”
Global Olive Oil Trade and Consumption
The global olive oil trade is booming, with the U.S. becoming a big player. In 2023, the U.S. became the second-biggest olive oil consumer, beating Spain16. Americans ate 375,000 tons of olive oil that year16.
Italy and Spain are still leading in olive oil use, but the U.S. is catching up fast. Italy used 410,000 tons, and Spain used 300,000 tons16. Prices in Spain went up a lot, making people eat 47% less olive oil in 202316.
Even though olive oil prices are high, the U.S. market is stable. Prices for extra virgin olive oil are over $10 per liter16. But, the private label olive oil is still affordable, thanks to special deals16.
Experts think the U.S. might soon be the biggest olive oil user by 203016. But, Spain’s big olive oil harvest might change that. Spain’s production could go back up to 1.4 million tons16.
Major Importers and Consumer Trends
Spain makes over 40% of the world’s olive oil17. But, prices have gone up a lot, especially in Spain. Olive oil costs a record 9.2 euros, or $9.84, per kilogram in Andalusia17. Droughts and high temperatures have caused big shortages, making prices even higher17.
The European olive oil market is expected to grow by 3%-5% each year18. Spain, Italy, Greece, Tunisia, Turkey, and Portugal make most of the world’s olive oil18. Imports in Europe have been growing by 3% a year from 2018 to 202218.
The olive oil trade is changing, with the U.S. and others playing bigger roles. As people look for healthier cooking oils, the market is set to grow. But, it will need new ideas and flexibility from producers and traders.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Olive oil production and use can greatly affect the environment, both good and bad. Olive trees are a renewable crop that helps with soil conservation and supports many species19. They use deep roots to find water underground, making them less dependent on scarce water resources19. Plus, they absorb carbon dioxide, helping to reduce greenhouse gases19.
But, making olive oil can also lead to waste and use a lot of water, which is bad for the planet if not handled right20. The process creates waste and wastewater, which can harm the environment20. Some methods produce less waste but create a hard-to-manage residue20.
20 Every year, the Mediterranean produces 30 million cubic meters of olive mill wastewater, and more waste is made than oil20. The waste from making olive oil is tough to break down and needs special treatment20.
As people want more olive oil, making it in a green way is key to lessen harm to the earth19. More farmers are using organic methods, which helps keep soil healthy19. Olive oil is also free from genetic engineering, supporting small farms and local economies19.
21 Making one liter of extra virgin olive oil removes about 10.65kg of carbon from the air, and it uses less water than many crops21. It’s also the greenest choice among cooking oils21.
The olive oil industry has big challenges in reducing its environmental impact because treating waste costs a lot20. There’s no unified way to deal with olive oil waste across different areas20. Some try to use the waste for good things, but it’s hard because it’s expensive and production is short20.
20 Getting rid of olive mill wastewater is a big problem, especially in poorer countries20. There are ways to clean it up, change how it’s made, and use parts of it again, but it’s still tough20.
“Olive oil production is less vulnerable to water scarcity compared to other crops, and olive trees act as natural carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.”19
Future Outlook and Challenges
The future of the global olive oil industry looks promising and challenging. The demand for high-quality olive oil is rising, especially in new markets outside the Mediterranean22. This trend could lead to significant growth. The market for Extra Virgin Olive Oil is expected to hit USD 2047.09 million by 2031, growing at 5.04% annually22.
But, the industry also faces big hurdles. Climate change could harm olive tree farming by changing weather and rainfall patterns23. Despite a 24% increase in production to 3.20 million tons in 2023/24, climate change could still impact this growth23. The industry needs to adopt more efficient and sustainable ways to produce olive oil24. Currently, production is about 21% lower than the last decade’s average, at 3,065,320 tons24.
There’s also a risk of fake or low-quality olive oil in the market, which is a big concern22. Extra virgin olive oil, the top grade, might struggle as organic and conventional types are more common22. Overcoming these challenges is key to the industry’s future success and meeting the increasing demand for olive oil.
FAQ
Which country is the world’s largest producer of olive oil?
Spain leads the world in olive oil production, making almost half of the global supply.
What are some of the other major olive oil producing countries?
Top producers include Italy, Turkey, Tunisia, Greece, Portugal, Morocco, Syria, Algeria, and Egypt, besides Spain.
What are the different varieties and qualities of olive oil?
Olive oil varieties range from extra virgin to refined, each with distinct properties and uses.
What factors contribute to Spain’s dominance in olive oil production?
Spain’s climate, large olive tree cultivation, advanced production, and strong trade ties help it lead in olive oil.
How does the global olive oil trade and consumption compare across different countries?
The U.S. imports most olive oil, but countries like Spain, Italy, and Greece consume more per person.
What are the environmental impacts and sustainability concerns related to olive oil production?
Olive oil production can be good or bad for the environment. Olive trees help with soil and biodiversity. But, it can also create waste and use a lot of water, which can harm the environment if not managed well.
What are the future challenges and opportunities for the global olive oil industry?
The future of olive oil looks complex, with both ups and downs. Growing demand for quality olive oil offers chances for growth. But, climate change, sustainable production, and fraud are challenges it faces.
Source Links
- U.S. Olive Oil Producers Achieve Record-Breaking Success at World Competition – https://www.oliveoiltimes.com/production/u-s-olive-oil-producers-achieve-record-breaking-success-at-world-competition/131584
- Which countries are the largest producers and exporters of olive oil? – https://9oliveres.com/en/blogs/noticias/que-paises-son-los-mayores-productores-y-exportadores-de-aceite-de-oliva
- Olive oil – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Olive_oil
- Italian olive oil scandal – leading brands accused of fraud – https://www.casaolea.com/blog/italian-olive-oil-scandal-leading-brands-accused-fraud
- Which Country Produces The Most Olives? – Global Top Stats – https://globaltopstats.com/which-country-produces-the-most-olives/
- Extra virgin olive oil: what it is, benefits and use – Sol Verona – https://solverona.com/en/olio-extravergine-doliva-cose-benefici-e-utilizzo/
- The truth about olive oil from Italy – https://exauoliveoil.com/blogs/olive-oil/truth-about-olive-oil-from-italy
- Olive oil production by country | Main producers – https://italicaoliveoil.com/olive-oil-production-by-country/
- Italian Producers Reveal Their Winning Strategies at World Competition – https://www.oliveoiltimes.com/production/italian-producers-share-their-secrets-to-success-at-world-competition/131411
- Greece and the World Celebrate UNESCO World Olive Tree Day – https://www.greekliquidgold.com/index.php/en/news/453-greece-and-the-world-celebrate-unesco-world-olive-tree-day
- Northern Hemisphere’s Best Extra Virgin Olive Oils Revealed – https://www.oliveoiltimes.com/world/northern-hemispheres-best-extra-virgin-olive-oils-revealed/131493
- Enipeas – https://www.bestoliveoils.store/pages/enipeas
- Olive oil production by country – https://www.aceitedelasvaldesas.com/en/faq/varios/produccion-aceite-de-oliva-por-paises/
- Producing 69% of the world’s production, the EU is the largest producer of olive oil – https://agriculture.ec.europa.eu/news/producing-69-worlds-production-eu-largest-producer-olive-oil-2020-02-04_en
- Olive oil quality by country | Around the world with 5 oils – https://italicaoliveoil.com/olive-oil-quality-country/
- US Surpasses Spain as Second-Largest Olive Oil Consumer – https://www.oliveoiltimes.com/business/north-america/us-surpasses-spain-as-second-largest-olive-oil-consumer/129458
- World’s largest olive oil producer says the industry faces one of its toughest moments ever – https://www.cnbc.com/2024/05/02/spains-deoleo-says-olive-oil-sector-faces-one-of-its-toughest-moments.html
- The European market potential for olive oil – https://www.cbi.eu/market-information/processed-fruit-vegetables-edible-nuts/olive-oil/market-potential
- Olive Oil: A Sustainable Choice for Earth-Conscious Consumers – https://www.aboutoliveoil.org/olive-oil-earth-day
- Environmental Impact of Olive Oil Processing Wastes – https://www.ecomena.org/olive-oil-wastes/
- How sustainable is extra virgin olive oil? | Olive Wellness Institute – https://olivewellnessinstitute.org/article/how-sustainable-is-extra-virgin-olive-oil/
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil Market Outlook 2024 : Trends, Challenges and Key Suppliers Analysis By 2031 – https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/extra-virgin-olive-oil-market-outlook-vgqef
- Global Olive Oil Production Predicted to Rebound – https://www.oliveoiltimes.com/world/global-olive-oil-production-predicted-to-rebound
- Global Production May Exceed Expectations, but Not Enough to Move Prices – https://www.oliveoiltimes.com/world/global-production-may-exceed-expectations-but-not-enough-to-move-prices/130498