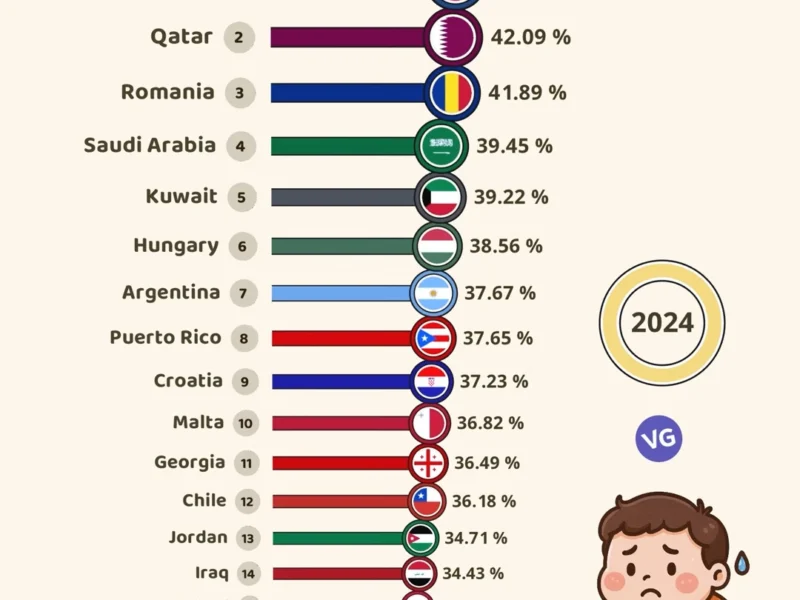
The Middle East is a key region that includes the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, and more. It’s been called the Middle East since the early 20th century, instead of the “Near East”.1 The area covers most of West Asia and includes Egypt and Turkey.1 Out of 18 countries in the Middle East, 13 belong to the Arab world.1 This region is known for its rich history, dating back to ancient times.1 It’s the birthplace of religions like Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.1 A mix of different people live here, with Arabs being the largest group. Then come Turks, Persians, Kurds, and many others.2
Key Takeaways
- The Middle East includes an important area with countries like those in the Arabian Peninsula and the Levant.
- The name “Middle East” was adopted in the 20th century to replace “Near East”.
- 13 out of 18 countries in the Middle East are part of the Arab world.
- It’s a place with a deep history, where religions such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam began.
- A mix of people live here, with Arabs making up the biggest part, followed by Turks, Persians, Kurds, and others.
Introduction to the Middle East
The Middle East is a region near the Mediterranean Sea. It includes the Arabian Peninsula and countries like Turkey, Egypt, and Iran. The term “Middle East” was first used in the 1850s by the British.1 It is located between North Africa, Southern Europe, and Central and Southern Asia.
Geographical Definition
This area is about 7,207,575 km2 big.2 It features deserts and mountains. The weather is mostly hot and dry. But some places have a Mediterranean climate, like the Levant and parts of Turkey.
Cultural and Historical Significance
The Middle East is very important in culture and history. It’s the birthplace of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.1 It’s also known as the “cradle of civilization.” This is where early human settlements and ancient civilizations emerged, such as Mesopotamia and Egypt.2 Over time, many empires and powers have fought for control here.
Major Countries in the Middle East
Egypt is a key country in the Middle East, placed at the northeast of Africa. With a large population, it boasts a deep cultural history. Its past goes back to ancient times. Known for the Pyramids of Giza and the Sphinx, Egypt also has a lively capital, Cairo. The Nile River’s importance to Egypt’s growth cannot be overstated.2
Saudi Arabia stands as the biggest Middle Eastern country. It is held in high regard as the birthplace of Islam. Mecca and Medina, its two holiest sites, see millions come for pilgrimage annually. A monarch, its global sway is largely due to its abundant oil resources.3
Iran holds significant power in the region. With a cultural legacy from ancient Persia, it is a theocratic republic. Here, the Supreme Leader influences the country greatly. Notable for its role in the region’s various conflicts and its nuclear initiatives, Iran’s impact on the Middle Eastern political scene is undeniable.1
Turkey, bridging Europe and Asia, has a strong foothold in the Middle East. A secular, democratic republic, it bears a diverse culture. Its prime location and economic prowess make Turkey a key figure in Middle Eastern politics.2
Country In The Middle East
The Middle East has many different landscapes and climates. It ranges from the dry deserts in the Arabian Peninsula to the high mountains in Iran and Turkey. Most of the area is dry and hot, but some places are cooler and get more rain, like the areas near the Mediterranean Sea. Major rivers like the Nile, Tigris, and Euphrates help with farming. They make a green area called the Fertile Crescent.2
Geography and Climate
The Middle East is big, covering about 7,207,575 km2 (2,782,860 sq mi).2 It has many different types of land, from the sandy deserts to the snowy mountains. The weather is mostly hot and dry, but some places by the Mediterranean Sea are cooler and wetter.2
Population and Demographics
Many different people live in the Middle East, but most are Arabs. You also find Turks, Persians, Kurds, and others. In 2010, the region had about 371 million people.2 Big cities like Istanbul and Cairo are important for business, culture, and politics.
Economy and Industry
The economy in the Middle East relies a lot on oil and gas. Countries like Saudi Arabia, Iran, and the United Arab Emirates export a lot of oil. This makes the region very important in world politics.1 Besides oil, the Middle East also has farming, factories, and tourism. These industries help the economy as well.2
The Middle East is important because of its location and resources, especially oil.1 Its mix of people, cultures, and politics play a big role in its growth. This brings both challenges and chances for the countries there.
Political Landscape
The Middle East’s political setup includes monarchies, republics, and theocracies. Places like Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates are monarchies. In contrast, Iran and Turkey are republics.
There’s been ongoing political instability and power struggles. Many groups fight for control within each country and across the region.
Government and Leadership
The Middle East is very important in world politics. Its countries often have arguments with each other.4 It has seen many conflicts like the Arab-Israeli fighting and the Iran-Iraq War.
The Syrian civil war is still happening today. Countries like the U.S., Russia, and some European nations are also involved. This makes everything more complex.
International Relations
5 The Abraham accords were signed in September 2020. They aimed to make relations better between Israel and Arab states.
In 1979, Egypt started talking to Israel. Jordan did the same in 1994. But, even after three years of the Abraham accords, the Israel-Palestine issue remains unsolved.
Saudi Arabia and Qatar do not have normal relations with Israel yet. If Saudi Arabia agrees to normal relations, it would be a significant moment. This would mean a symbolic end to the Arab-Israeli wars of the 20th century.
The UAE and Qatar have also put money into the West Bank. This shows they have some influence in the region.
Cultural Heritage
The Middle East is the starting place of major religions like Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.6 Its culture is closely connected to these faiths. They influence everything from traditions to daily life. This includes holy places in Jerusalem and Muslim pilgrimages to Mecca and Medina.
The diverse religious culture in the Middle East is a big part of its identity.
Religion and Traditions
The region’s religious history is seen in its varied traditions and customs.7 Almost every country there has a UNESCO World Heritage Site, with a focus on religious history.7 For instance, the Kadisha Valley in Lebanon has Christian monasteries built on cliffs.
Islamic Cairo’s Takiyyat al-Gulshani, from the sixteenth century, is another example. It shows the lasting impact of religion on the region’s culture.6
Art and Architecture
The Middle East’s artistic and architectural scene is diverse and influential.6 Think of the Egyptian pyramids and Islamic mosques. Also, consider the beauty of Ottoman palaces. These are just some examples of the region’s creative heritage.7
Its traditional crafts like calligraphy, pottery, textiles, and metalwork are still cherished.
The Middle East’s heritage is a mix of cultures that spans 5,000 years.6 It is rich in history, religion, and art. This blend makes the region fascinating for both tourists and scholars.
Tourism Hotspots
The Middle East is full of ancient wonders that draw people worldwide. There’s the Pyramids of Giza in Egypt8. Then, the breathtaking Petra in Jordan8, the Hagia Sophia in Turkey8, and Jerusalem’s sacred sites. These places are rich with history and things to see, making them a must-visit for those interested in culture and heritage.
Yet, the Middle East isn’t just about its ancient past. It’s also a land of diverse natural beauty. You can explore the Red Sea’s coast, the stunning Arabian landscapes, and find snow in places like Turkey and Iran. Must-see places include the Dead Sea, Jordan’s Wadi Rum desert8, and Turkey’s unique Cappadocia region9.

Geopolitical Challenges
The Middle East is no stranger to conflict and tensions. These stem from the Arab-Israeli conflict to civil wars in Syria and Yemen. Tensions between Iran and countries like Saudi Arabia also play a role. This has created much instability and violence that affect not only security but also the people in the region.10
Conflicts and Tensions
Environmental issues are a big deal in the Middle East. Water scarcity, desertification, and climate change impacts are problems. The region heavily uses fossil fuels, making a big mark on global climate change. Its dry climate and limited water sources cause ongoing disputes about water use.10
Environmental Concerns
Since October 17th, Houthis have attacked US troops in Syria and Iraq about 130 times. US and UK forces countered with strikes on Houthis, protecting commercial ships. Iran-backed militias could fight Israel directly in Lebanon. Almost 10% of world trade goes through the Red Sea and Suez Canal. Smuggling is rising along the Jordanian-Syrian border, growing in scale and products.10
The region also deals with political instability and tension. Issues include the Israel-Iran conflict and the Saudi-Iran rivalry. Arab countries have border problems, which stall economic development plans.11
Key players shaping the Middle East include Saudi Arabia, Iran, Turkey, Israel, the US, and Russia. China is also making moves in the region. Iran and Saudi Arabia work to control each other’s influence. Israel is keen on stopping Iran’s nuclear and regional ambition. It also aims for peace with Palestinians. Turkey is actively engaging with the Middle East. Russia looks to increase its power against the US’s interests.12
Investment Opportunities
The Middle East provides many chances for investing, despite challenges. Especially in energy, infrastructure, and real estate. With over $8,500 billion from oil and gas in 2022, it’s a hotspot for global investors.13 Its growing economies and middle class offer more opportunities. Sectors like ICT, eCommerce, and educational technology are growing fast. The MENA ICT market will hit $250.2 billion by 2029. The educational tech and smart classrooms market in MEA will top $7,626.1 million by 2027.13
The Middle East’s location and progress open doors in tourism, logistics, and green energy. By 2031, the UAE aims for 40 million hotel guests. And Saudi Arabia wants tourism to be 10% of its GDP by 2030.14 Additionally, the region plans to cover almost a quarter of its primary energy needs with renewables by 2050. In the power sector, renewables are set to top half of the energy mix. This offers chances in the green hydrogen and renewable energy fields.14
Dubai, Cairo, and other cities in the region are now big business hubs. They’re great for starting new businesses. Plus, they provide routes to reach the bigger Middle Eastern and North African markets.13
| Country | Market Size (in billions) |
|---|---|
| Saudi Arabia | $13.0 |
| Turkey | $12.5 |
| UAE | $10.7 |
The Middle East is key for investments. Its growing economies and diversity efforts make it perfect for smart investors. They can use the region’s potential for great returns.131514
Future Prospects
Economic Development
The Middle East’s future is about changing its economy to be more varied and sustainable. It used to rely heavily on selling oil and gas for economic growth. Now, it aims to invest more in areas like green energy, making products, and various services.16
Building better roads, schools, and hospitals is key. So is attracting businesses from other countries to invest. These steps are vital for the long-term health of the region’s economy.
Social and Political Reforms
There’s also a big push for change in the Middle East’s society and politics. This involves dealing with big issues like human rights, equal rights for all, and how people are represented in government.17
Some places in the Middle East have seen a lot of tension because of these issues in recent years. These events show the deep wish for more democracy and for solving big social and economic problems. The success of these changes is key to the region becoming more stable and prosperous.
Conclusion
The Middle East is very complex and important globally. It has a rich cultural heritage and diverse people. It plays a big role in worldwide politics. The Middle East faces many issues and changes. Its future matters a lot to the world.18
The book’s conclusion looks at a model for understanding the region’s order. It’s useful in seeing what has changed since World War I. The book raises questions about how the Middle East evolves. This knowledge helps us aim for a better future for everyone.18
The book covers topics like regional order, authoritarianism, and sovereignty in the Middle East. It also discusses IR theories. The Middle East has changed a lot through history. Despite stereotypes, it’s contributing a lot to science worldwide.19
The book is from 2021 and is by Cambridge University Press. People often think the Middle East was more advanced in the past. This view is not entirely true. It ignores the region’s present achievements and dynamic culture.18
Different places and people in the Middle East show unique cultures. Recognizing these differences is key. It helps us understand the region better.18
FAQ
What is the Middle East and where is it located?
The Middle East includes countries like Egypt, Iran, and Turkey. This area sits between North Africa and Southern Europe.
What are the major countries in the Middle East?
Some of the big countries in the Middle East are Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and Iran. Others include Iraq, Syria, and the United Arab Emirates.
What is the cultural and historical significance of the Middle East?
It’s where three main religions began: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. This area is also the cradle of some of the first human civilizations.
What are the main ethnic groups in the Middle East?
Important ethnic groups here are Arabs, Turks, and Persians. You can also find Kurds, Jews, and Assyrians living there.
What is the political landscape of the Middle East?
The Middle East has many different types of governments. Some are monarchies, some are republics, and some are theocracies. It often faces political unrest and power struggles.
What are the major environmental challenges facing the Middle East?
This region struggles with water shortages and climate change. Overusing fossil fuels also affects the whole world’s climate.
What are the investment opportunities in the Middle East?
There are big chances to invest in the Middle East, especially in energy and real estate. The area’s oil and gas resources draw global investors.
What are the future prospects for the Middle East?
The Middle East needs to make its economy more varied and eco-friendly. It aims to update its infrastructure and public services. These steps will help its future growth and stability.
Source Links
- https://www.britannica.com/place/Middle-East
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_East
- https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/middle-east-countries
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Democracy_in_the_Middle_East_and_North_Africa
- https://theconversation.com/israel-gaza-conflict-how-could-it-change-the-middle-easts-political-landscape-expert-qanda-215473
- https://www.wmf.org/blog/travelogue-cultural-heritage-middle-east
- https://www.middleeasteye.net/discover/eight-unesco-heritage-sites-middle-east-you-should-know-about
- https://traveltriangle.com/blog/places-to-visit-in-middle-east/
- https://www.roughguides.com/article/most-beautiful-places-in-the-middle-east/
- https://www.geopoliticalmonitor.com/bracing-for-middle-east-instability/
- https://carnegieendowment.org/research/2024/03/the-geopolitics-of-economic-development-in-the-middle-east?center=middle-east
- https://www.brookings.edu/articles/the-new-geopolitics-of-the-middle-east-americas-role-in-a-changing-region/
- https://www.apptunix.com/blog/business-opportunities-middle-east/
- https://virtuzone.com/blog/top-business-opportunities-in-the-middle-east/
- https://www.forbes.com/uk/advisor/investing/how-to-invest-in-the-middle-east-and-africa/
- https://www.worldbank.org/en/region/mena/publication/middle-east-and-north-africa-economic-update
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/future-work-middle-east-staying-ahead-curve-iraif
- https://ohiostate.pressbooks.pub/key2mideast/chapter/conclusion/
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/international-relations-in-the-middle-east/conclusion/88E264711D01C68EB7E1A41D96D96B58