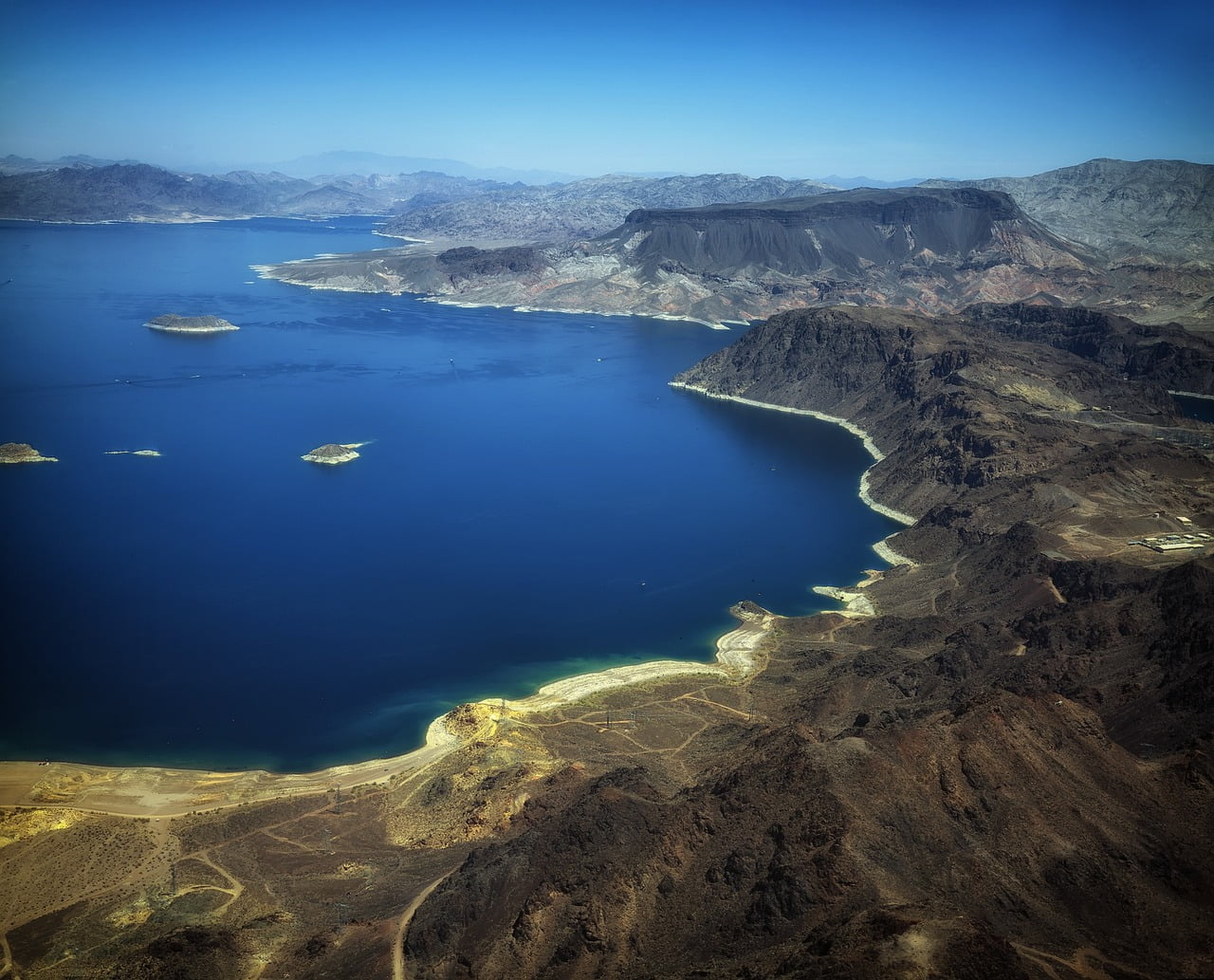
The captivating and ever-evolving story of Lake Mead’s water levels has become a subject of immense significance, not just for the Southwestern United States, but for the entire nation. As the largest reservoir in the country, Lake Mead’s fortunes are intricately linked to the well-being of the region, making its ebbs and flows a matter of paramount concern.
| DATE MEASURED | ELEVATION | CHANGE | CONTENT | INFLOW (cfs) | OUTFLOW (cfs) | HIGH TEMP | LOW TEMP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sun, Apr 07, 2024 | 1074.66 | -0.02 | 9,573,420 | 11693 | 13780 | 62.5 | 48.5 |
| Sat, Apr 06, 2024 | 1074.68 | -0.08 | 9,575,042 | 11747 | 15870 | 60.6 | 42.2 |
| Fri, Apr 05, 2024 | 1074.76 | -0.20 | 9,581,528 | 11585 | 17188 | 54.2 | 43.8 |
| Thu, Apr 04, 2024 | 1074.96 | -0.20 | 9,597,744 | 11288 | 16954 | 73.6 | 55.6 |
| Wed, Apr 03, 2024 | 1075.16 | -0.10 | 9,613,983 | 10997 | 14063 | 76.6 | 55.9 |
| Tue, Apr 02, 2024 | 1075.26 | -0.07 | 9,622,000 | 11945 | 13400 | 71.3 | 52.8 |
| Mon, Apr 01, 2024 | 1075.33 | -0.02 | 9,627,790 | 12694 | 15807 | 64.9 | 47.9 |
| Sun, Mar 31, 2024 | 1075.35 | 0.05 | 9,629,415 | 12577 | 11048 | 58.0 | 43.7 |
| Sat, Mar 30, 2024 | 1075.30 | -0.02 | 9,625,354 | 12762 | 12264 | 55.1 | 46.7 |
| Fri, Mar 29, 2024 | 1075.32 | -0.07 | 9,626,978 | 12439 | 14404 | 67.0 | 49.5 |
| Thu, Mar 28, 2024 | 1075.39 | -0.06 | 9,632,663 | 12035 | 14100 | 69.6 | 52.8 |
| Wed, Mar 27, 2024 | 1075.45 | -0.08 | 9,637,537 | 11248 | 13228 | 69.4 | 50.0 |
| Tue, Mar 26, 2024 | 1075.53 | 0.00 | 9,644,040 | 12287 | 11262 | 66.2 | 49.2 |
| Mon, Mar 25, 2024 | 1075.53 | 0.01 | 9,644,040 | 12478 | 10937 | 64.3 | 48.4 |
| Averages of List | 1075.19 | -0.06 | 9,616,538 | 11983.9 | 13878.9 | 65.2 | 49.1 |
Source: Lake Mead Water Database
Source: U.S. Lakes
The Significance of Lake Mead
Understanding the Importance of Lake Mead
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ig9UEPys2HALake Mead is a true jewel of the American West, a testament to the visionary engineering feats of the past. Formed by the construction of the iconic Hoover Dam, this mammoth body of water has long been a vital source of water, hydroelectric power, and recreational opportunities for millions of people. Its significance cannot be overstated, as it serves as a crucial cog in the intricate system that sustains the region’s delicate balance.
Lake Mead’s Role in the Southwestern Water Supply
As the primary water storage facility for the Colorado River, Lake Mead plays a pivotal role in meeting the water demands of the Southwestern United States. From bustling metropolises to thriving agricultural communities, the region’s prosperity is inextricably linked to the steady flow of water that originates from this vast reservoir. Understanding the gravity of this responsibility is essential in navigating the challenges that lie ahead.
The Declining Water Levels
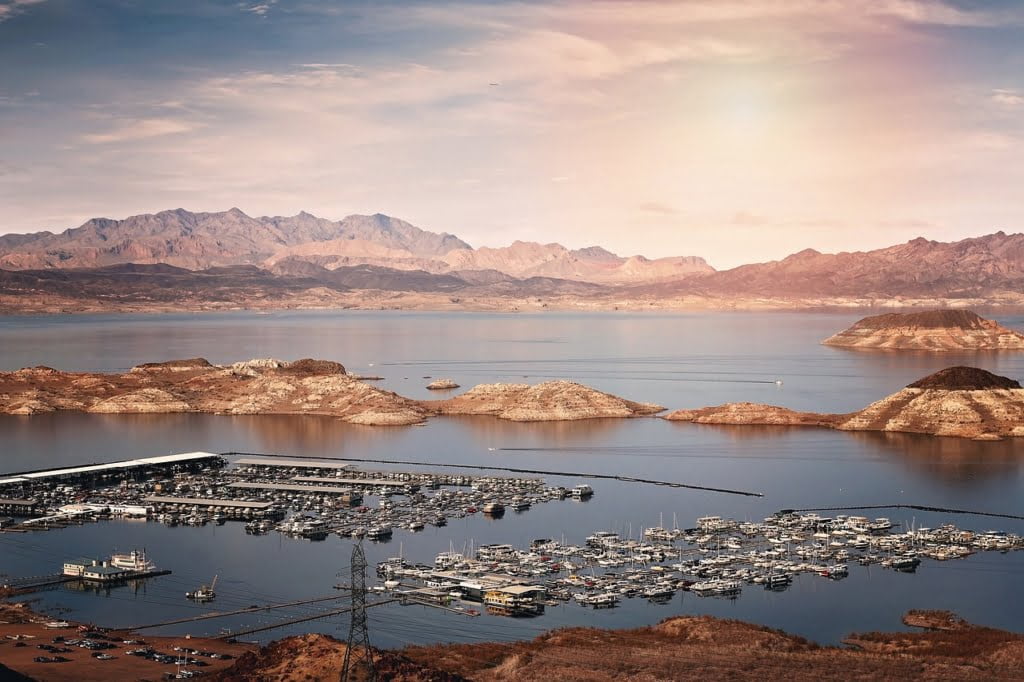

Tracking the Downward Trend
Over the past decades, the water levels at Lake Mead have been on a discernible downward trajectory, raising alarm bells among water managers, policymakers, and concerned citizens alike. The stark reductions in the reservoir’s content, as meticulously recorded in elevation measurements, paint a sobering picture of the ongoing water crisis.
Factors Contributing to the Water Level Drop
The causes behind the declining water levels are multifaceted, with a confluence of factors converging to exacerbate the situation. Persistent drought conditions in the Colorado River basin, the primary source of the reservoir’s water, have led to a steady diminishment of inflows. Coupled with this, the insatiable thirst of growing populations in the Southwestern states has placed an ever-increasing demand on the finite water resources, further straining the delicate balance.
Drought Conditions in the Colorado River Basin
The Colorado River basin, the lifeblood of the Southwestern United States, has been grappling with a prolonged and unrelenting drought, the effects of which have reverberated throughout the region. As snowpack levels in the Rocky Mountains continue to decline, the primary source of the river’s replenishment has dwindled, leading to a cascading impact on the water levels of Lake Mead.
Increased Water Demand from Growing Populations
The Southwestern states have witnessed a surge in population growth over the past decades, fueling a corresponding rise in water consumption. From burgeoning urban centers to thriving agricultural hubs, the insatiable thirst of these expanding communities has placed an immense strain on the region’s finite water resources, with Lake Mead bearing the brunt of this increased demand.
Climate Change and its Impact
Looming over these immediate challenges is the long-term spectre of climate change, which has exacerbated the drought conditions and further compounded the water scarcity issues facing Lake Mead. As the global climate continues to shift, the region’s water landscape is likely to become increasingly volatile, necessitating a comprehensive rethinking of water management strategies.
Monitoring Lake Mead’s Water Levels
Accessing Real-Time Data
Tracking the ebbs and flows of Lake Mead’s water levels has become a vital task, with water managers and concerned citizens alike closely monitoring the latest data. Through the utilization of advanced monitoring systems and comprehensive data repositories, stakeholders can stay abreast of the reservoir’s ever-changing conditions, enabling informed decision-making and proactive planning.
Interpreting the Elevation Measurements
The elevation of Lake Mead, measured in feet above sea level, serves as a crucial indicator of the reservoir’s water content and overall health. By closely examining these elevation readings, experts can glean valuable insights into the reservoir’s trajectory, informing discussions and guiding the implementation of effective water management strategies.
Analyzing the Content and Inflow/Outflow Rates
Alongside the elevation measurements, the continuous monitoring of Lake Mead’s water content and the rates of inflow and outflow provide a comprehensive understanding of the reservoir’s dynamics. These data points shed light on the delicate balance between supply and demand, empowering policymakers and water managers to make informed decisions that safeguard the region’s water security.
The Ripple Effect of Low Water Levels
Impacts on Hydroelectric Power Generation
As the water levels in Lake Mead decline, the reservoir’s ability to generate hydroelectric power through the Hoover Dam is significantly affected. This reduction in power output can have far-reaching consequences, impacting the energy grid and necessitating the exploration of alternative power sources to meet the region’s growing demands.
Implications for Agricultural and Urban Water Use
The scarcity of water in Lake Mead has profound implications for both agricultural and urban water users. Farmers and ranchers may face reduced water allocations, threatening the viability of their operations and the regional food supply. Similarly, urban centers reliant on the reservoir’s water may be compelled to implement stringent conservation measures, altering the way residents and businesses consume this precious resource.
Ecosystem Changes and Environmental Concerns
The declining water levels in Lake Mead have also triggered significant ecological changes, affecting the delicate balance of the reservoir’s aquatic ecosystems. The exposure of previously submerged land and the potential for altered water quality can have far-reaching consequences for the region’s flora and fauna, underscoring the need for comprehensive environmental impact assessments and proactive conservation efforts.
Strategies for Water Conservation
Residential Water-Saving Measures
Empowering individuals and households to adopt water-saving practices is a crucial component of the broader strategy to address the water crisis. From the installation of water-efficient appliances to the implementation of drought-tolerant landscaping, residents can play a vital role in reducing overall water consumption and mitigating the strain on Lake Mead.
Agricultural Efficiency Improvements
The agricultural sector, a major consumer of water in the Southwestern United States, must also explore innovative solutions to enhance water-use efficiency. This may involve the adoption of advanced irrigation techniques, the cultivation of drought-resistant crops, and the implementation of precision farming methodologies, all of which can contribute to the sustainable management of the region’s water resources.
Innovative Water Management Policies
Ultimately, the long-term solution to the water crisis facing Lake Mead will require the development and implementation of cutting-edge water management policies. This may involve the implementation of water rights trading systems, the exploration of desalination technologies, and the promotion of water recycling and reuse initiatives, all of which can help to alleviate the pressure on the reservoir.
Projections and Future Scenarios
Potential Drought Resilience Efforts
As the region grapples with the ongoing drought, the need for comprehensive drought resilience strategies becomes increasingly paramount. This may involve the development of early warning systems, the diversification of water sources, and the implementation of advanced water conservation technologies, all of which can help to mitigate the impacts of prolonged dry periods on Lake Mead and the surrounding communities.
Adaptation Strategies for Water Scarcity
Looking ahead, the Southwestern United States must devise and implement robust adaptation strategies to address the looming challenge of water scarcity. This may involve the exploration of alternative water sources, the optimization of water infrastructure, and the fostering of cross-jurisdictional cooperation, all of which can contribute to the long-term sustainability of the region’s water resources.
Exploring Alternative Water Sources
In the face of dwindling water levels in Lake Mead, the exploration of alternative water sources becomes a crucial priority. This may include the investigation of groundwater resources, the expansion of water recycling and reuse programs, and the consideration of large-scale desalination projects, all of which can help to diversify the region’s water portfolio and enhance its resilience to future water challenges.
The Role of Hoover Dam in Lake Mead
Hoover Dam’s Influence on Water Levels
The iconic Hoover Dam, which gave birth to Lake Mead, continues to play a pivotal role in the management and regulation of the reservoir’s water levels. The dam’s operations, including the release of water downstream, have a direct impact on the overall content and elevation of the lake, underscoring the delicate balance that must be struck between water storage, hydropower generation, and the region’s diverse water needs.
Managing the Dam’s Operations and Releases
The intricate task of managing the Hoover Dam’s operations and water releases is a critical component of the broader effort to maintain the stability of Lake Mead’s water levels. Water managers must carefully navigate the competing demands for water, hydroelectric power, and environmental considerations, ensuring that the dam’s operations align with the long-term sustainability of the region’s water resources.
Comparing Lake Mead and Lake Powell
Exploring the Dynamics Between the Two Reservoirs
Lake Mead and Lake Powell, the two largest reservoirs in the Colorado River system, are inextricably linked, with their fortunes ebbing and flowing in tandem. Understanding the dynamic relationship between these two critical water bodies is essential in crafting comprehensive water management strategies for the region.
Implications of Fluctuating Water Levels in Both Lakes
The interplay between the water levels in Lake Mead and Lake Powell has far-reaching implications for the Southwestern United States. As the two reservoirs experience fluctuations in their content, the impacts can ripple throughout the region, affecting water supply, hydroelectric power generation, and the overall resilience of the Colorado River basin.
Historical Perspectives on Lake Mead
Tracing the Lake’s Development and Importance
The story of Lake Mead is one of human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of water security in the arid Southwest. From its inception, the lake has stood as a testament to the vision and engineering prowess of those who sought to harness the power of the Colorado River, transforming it into a vital resource that has supported the region’s growth and prosperity for generations.
Significant Events and Milestones in Lake Mead’s History
Lake Mead’s history is punctuated by a series of significant events and milestones, each one contributing to the evolving narrative of the reservoir’s importance. From the completion of the Hoover Dam to the periodic fluctuations in water levels, these moments have shaped the way we understand and interact with this monumental water body, informing our efforts to safeguard its future.
Recreational Activities and the Changing Shoreline
Adapting to the Shifting Waterline
As the water levels in Lake Mead continue to fluctuate, the shifting shoreline poses a unique challenge for the region’s recreational activities. From boating and fishing to camping and hiking, the receding waterline has forced the adaptation of these beloved pastimes, requiring innovative solutions to ensure the continued enjoyment of the lake’s natural splendor.
Preserving Recreational Opportunities
The preservation of recreational opportunities at Lake Mead is not merely a matter of convenience, but a vital component of the region’s economic and social fabric. Water managers, policymakers, and community stakeholders must work in tandem to develop strategies that maintain the viability of these activities, ensuring that the lake remains a cherished destination for generations to come.
The Economic Impact of Lake Mead’s Water Levels
Tourism and Boating Industry Considerations
The tourism and boating industries that thrive on the shores of Lake Mead are deeply intertwined with the reservoir’s water levels. As the water recedes, these sectors face significant challenges, from the relocation of marinas to the dwindling of visitor numbers. Addressing the economic implications of these changes is crucial in safeguarding the livelihoods of those who depend on the lake’s prosperity.
Potential Impacts on Businesses and Local Economies
The ripple effects of Lake Mead’s water level fluctuations extend far beyond the recreational sector, reaching into the broader economic landscape of the region. Businesses ranging from agricultural enterprises to service providers may face disruptions, while local economies grapple with the consequences of this water crisis. Navigating these challenges requires a comprehensive understanding of the interconnected nature of the lake’s fortunes and the regional economy.
Collaboration and Water Management Efforts
Interstate Cooperation and Policy Discussions
Addressing the complex water challenges facing Lake Mead and the Colorado River basin necessitates a collaborative approach, with stakeholders from multiple states coming together to devise innovative solutions. From interstate compacts to policy discussions, these cooperative efforts are essential in ensuring the equitable and sustainable management of the region’s finite water resources.
Stakeholder Engagement and Public Participation
Effective water management strategies must be informed by the diverse perspectives and concerns of the region’s stakeholders, including local communities, environmental advocates, and industry representatives. By fostering meaningful engagement and public participation, water managers can develop holistic and inclusive policies that address the needs of all those who depend on the water resources provided by Lake Mead.
Technological Advancements in Water Conservation
Innovative Solutions for Efficient Water Use
As the challenges facing Lake Mead and the Colorado River basin continue to evolve, the need for innovative solutions to water conservation becomes increasingly pressing. From the development of advanced irrigation systems to the implementation of smart water-monitoring technologies, the region’s water managers must embrace the power of cutting-edge solutions to maximize the efficiency and sustainability of water use.
Emerging Desalination and Water Recycling Technologies
In the face of dwindling freshwater resources, the exploration of alternative water sources, such as desalination and water recycling, has emerged as a critical focus area. The advancement of these technologies holds the promise of diversifying the region’s water portfolio, reducing the strain on Lake Mead and bolstering the long-term resilience of the Southwestern United States.
Environmental Concerns and Ecosystem Resilience
Protecting Fragile Habitats and Wildlife
The declining water levels in Lake Mead have profound implications for the delicate ecosystems that call the reservoir home. From the exposure of previously submerged habitats to the disruption of aquatic food webs, the ecological consequences of this water crisis must be addressed with utmost care and consideration. Safeguarding the region’s fragile environments and the diverse species that depend on them is a critical priority.
Addressing the Ecological Consequences of Water Scarcity
As the water scarcity issues facing Lake Mead continue to escalate, the need to address the broader ecological consequences becomes increasingly paramount. Water managers, policymakers, and environmental advocates must collaborate to develop comprehensive strategies that mitigate the impact of water shortages on the region’s natural systems, ensuring the long-term resilience of these precious resources.
Community Outreach and Education
Raising Awareness about Water Conservation
Engaging the public in the effort to address the water crisis facing Lake Mead is a crucial component of any comprehensive solution. Through targeted outreach and educational campaigns, water managers can empower communities to adopt water-saving practices, foster a culture of conservation, and become active participants in the stewardship of the region’s water resources.
Engaging the Public in Sustainable Water Practices
Beyond merely raising awareness, the successful navigation of the water challenges confronting Lake Mead will require the active participation of the region’s residents and businesses. By providing the tools, resources, and incentives for the adoption of sustainable water practices, water managers can harness the collective power of the community to drive meaningful change and ensure the long-term viability of the Southwestern United States’ water supply.
The Future of Lake Mead and the Colorado River Basin
Long-Term Sustainability Challenges
As the region looks to the future, the challenges facing Lake Mead and the broader Colorado River basin loom large. From the persistent threat of drought to the looming specter of climate change, the path to long-term sustainability will require a comprehensive and multifaceted approach, one that balances the competing demands of the region’s diverse stakeholders.
Adapting to a Changing Climate and Water Landscape
The Southwestern United States is poised to confront a future marked by heightened uncertainty and volatility in its water resources. Adapting to these shifting conditions will necessitate the development of adaptive and resilient water management strategies, drawing upon the latest scientific data, technological advancements, and collaborative approaches to ensure the region’s long-term water security.