The future of life expectancy in Europe looks interesting by 2025. The United Nations says Europeans will live about 79.09 years on average. But, this number hides the big changes happening in how long people live.
Looking at life expectancy in Europe in 2025 is more than just numbers. Experts see these numbers as signs of how healthy a society is. They also show the economic and healthcare challenges we might face.
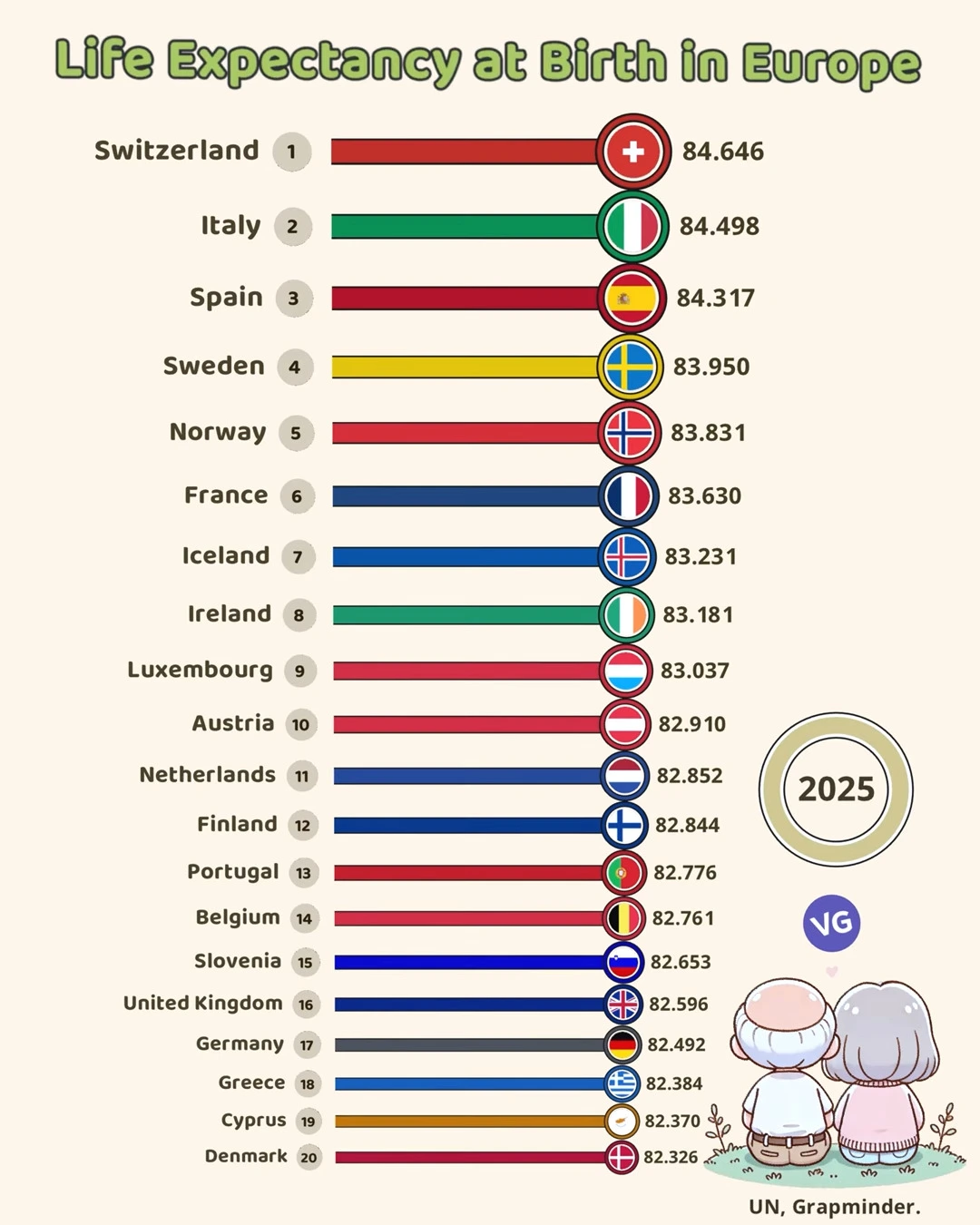
Projections for Life Expectancy in Europe by 2025
| Rank | Country | Life Expectancy | Flag |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Switzerland | 84.646 | 🇨🇭 |
| 2 | Italy | 84.498 | 🇮🇹 |
| 3 | Spain | 84.317 | 🇪🇸 |
| 4 | Sweden | 83.950 | 🇸🇪 |
| 5 | Norway | 83.831 | 🇳🇴 |
| 6 | France | 83.630 | 🇫🇷 |
| 7 | Iceland | 83.231 | 🇮🇸 |
| 8 | Ireland | 83.181 | 🇮🇪 |
| 9 | Luxembourg | 83.037 | 🇱🇺 |
| 10 | Austria | 82.910 | 🇦🇹 |
| 11 | Netherlands | 82.852 | 🇳🇱 |
| 12 | Finland | 82.844 | 🇫🇮 |
| 13 | Portugal | 82.776 | 🇵🇹 |
| 14 | Belgium | 82.761 | 🇧🇪 |
| 15 | Slovenia | 82.653 | 🇸🇮 |
| 16 | United Kingdom | 82.596 | 🇬🇧 |
| 17 | Germany | 82.492 | 🇩🇪 |
| 18 | Greece | 82.384 | 🇬🇷 |
| 19 | Cyprus | 82.376 | 🇨🇾 |
| 20 | Denmark | 82.326 | 🇩🇰 |
Longevity trends show that life expectancy might stay the same, but there are many factors at play. Medical progress, lifestyle changes, and differences in regions all affect how long people live. The number 79.09 is a mix of science, society, and economy.
People making policies, working in healthcare, and planning for the future use these numbers. They help plan for the needs of an aging population. Even though life expectancy seems steady, there are big changes in healthcare and technology that affect how long we live.
Current State of Life Expectancy in Europe
European demographics show a complex picture of longevity. Life expectancy at birth in the European Union is 80.6 years. There are big differences between genders and countries.
Healthy life years vary across regions. Western European nations have higher life expectancy rates. This is different from Eastern European countries.
Regional Variations in Life Expectancy
Life expectancy in Europe varies a lot:
- Western European countries like Switzerland and Spain reach around 83-84 years
- Eastern European nations such as Ukraine and Russia hover around 74-75 years
- Nordic countries maintain consistently high life expectancy rates
Gender-Specific Life Expectancy Patterns
Gender is key in life expectancy:
- Women: Average life expectancy of 83.3 years
- Men: Average life expectancy of 77.9 years
- Persistent gap of approximately 5.4 years between genders
Impact of Recent Global Events on Mortality Rates
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly disrupted traditional life expectancy projections across European regions.
Global health events have brought new challenges to European demographics. The pandemic lowered life expectancy and showed health weaknesses in different groups.
Knowing these details helps policymakers and healthcare workers. They can make better plans to improve health and fix regional gaps.
Life Expectancy in Europe 2025: Key Projections and Statistics
The future of life expectancy in Europe is complex and changing. The United Nations says the average life expectancy in 2025 will be 79.09 years. This shows how healthcare and quality of life are getting better.
Looking at the aging population and longevity trends, we see big differences across Europe. Here’s a detailed look at what’s expected:
- Southern European countries like Spain and Italy are still leading in life expectancy.
- Northern European nations are seeing steady improvements in health outcomes.
- Eastern European countries are slowly but surely increasing their life expectancy.
When it comes to gender, women in the European Union are expected to live longer. They are projected to live an average of 82.9 years, while men are expected to live 77.2 years.
| Country | Projected Life Expectancy 2025 | Gender Gap |
|---|---|---|
| Spain | 83.3 years | 5.7 years |
| Sweden | 83.1 years | 5.2 years |
| Italy | 82.7 years | 5.5 years |
| Bulgaria | 71.4 years | 4.8 years |
Emerging healthcare innovations and public health initiatives are expected to play a crucial role in driving these life expectancy projections forward.
“The future of European longevity lies in our commitment to preventive healthcare and quality of life improvements.” – European Health Research Institute
Historical Trends in European Life Expectancy (1950-2024)
Over the last 70 years, European demographics have seen big changes in life expectancy. This period shows how medicine, society, and technology have improved a lot.
Decades of Progress: Major Milestones
Europe’s journey in longevity is truly impressive. Some major highlights include:
- Post-World War II healthcare system improvements
- Dramatic reduction in infant mortality rates
- Advanced medical treatments and technologies
- Improved public health initiatives
Factors Behind Historical Improvements
Several key factors led to the big jump in life expectancy:
| Period | Life Expectancy | Key Developments |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 61.96 years | Post-war reconstruction |
| 1980 | 71.23 years | Advanced medical technologies |
| 2024 | 79.30 years | Comprehensive healthcare systems |
Life expectancy has risen by 27.99% from 1950 to 2024. This means people now live about 17.34 years longer. This growth is thanks to better healthcare, higher living standards, and new medical discoveries.
“The story of European life expectancy is a testament to human resilience and scientific progress.” – European Health Research Institute
Gender Gap Analysis in European Longevity
The landscape of life expectancy in Europe 2025 shows a complex picture. There is a big gap between male and female life expectancies across European countries.
Key insights into the gender disparities in healthy life years include:
- Women in the EU have a life expectancy of 83.3 years compared to men’s 77.9 years
- The current gender gap stands at 5.4 years
- Healthy life years differ slightly, with women at 62.8 years and men at 62.4 years
Regional variations show big differences in longevity patterns:
| Country | Women’s Life Expectancy | Men’s Life Expectancy | Gap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spain | 85.9 years | 81.4 years | 4.5 years |
| Bulgaria | 77.9 years | 69.4 years | 8.5 years |
Biological and lifestyle factors contribute significantly to these differences. Men face higher risks from heart diseases, lifestyle health challenges, and dangerous work environments.
“The gender gap in life expectancy reflects complex interactions between genetic, social, and environmental factors.” – European Health Research Institute
Future projections show the gap might narrow. Healthcare improvements and lifestyle changes will play big roles in future life expectancy.
Regional Disparities in European Life Expectancy
European life expectancy shows a complex picture of regional differences. These differences highlight unique challenges in demographics and healthcare across the continent.
Looking at life expectancy in European regions, we see big differences:
- Northern European regions have higher life expectancy rates
- Southern European countries have moderate longevity
- Eastern European regions face big healthcare challenges
- Western European nations have stable mortality trends
Northern vs Southern European Patterns
There are big differences between northern and southern Europe. The Scandinavian countries are among the top in life expectancy. Sweden and Norway stand out with their long life spans.
| Region | Life Expectancy (Years) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Madrid, Spain | 85.2 | Highest regional life expectancy |
| Severozapaden, Bulgaria | 72.3 | Lowest regional life expectancy |
Eastern European Life Expectancy Challenges
Eastern European regions face big health challenges. Historical and socioeconomic factors, along with limited healthcare, lead to lower life expectancy.
“The journey towards improved longevity in Eastern Europe requires sustained investment in healthcare and social development.”
Western European Mortality Trends
Western European regions have more stable mortality trends. They benefit from advanced healthcare and higher standards of living. Countries like France, Germany, and the Netherlands keep high life expectancy levels.
These regional differences highlight the need for targeted healthcare and social policies. They help address the unique challenges faced by different European regions.
Impact of Healthcare Systems on Life Expectancy
European healthcare systems are key in shaping life expectancy. The quality, access, and funding of these systems affect healthy life years in various countries.
Studies show big differences in healthcare that affect how long we live. Countries with strong universal healthcare see steady increases in life expectancy. On the other hand, those with broken medical systems do not.
“Healthcare quality is the cornerstone of population longevity” – European Health Research Institute
- Universal healthcare coverage increases life expectancy by standardized coefficient of 0.34
- Child vaccination programs boost healthy life years
- Preventive medicine strategies reduce long-term health complications
New healthcare innovations are changing life expectancy. Advanced tests, personalized medicine, and big public health efforts are leading to better health outcomes.
| Healthcare Indicator | Impact on Life Expectancy |
|---|---|
| Universal Health Coverage | +0.34 standardized coefficient |
| Child Vaccination (DPT-3) | +0.17 standardized coefficient |
| Sanitation Coverage | +0.31 standardized coefficient |
The future of European healthcare systems will be defined by their ability to adapt to changing demographic challenges and integrate cutting-edge medical technologies.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Future Life Expectancy
Lifestyle choices are key in shaping longevity trends in Europe. The link between personal habits and life expectancy offers deep insights. It shows how lifestyle affects chronic disease and health outcomes.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption Impact
Lifestyle factors have a big impact on life expectancy. For men, smoking cuts life short by 3.4 years. Drinking alcohol reduces it by 1.8 years.
Women see similar effects but less severe. Smoking shortens life by 0.8 years, and alcohol by 0.5 years.
- Smoking reduces male life expectancy significantly
- Alcohol consumption negatively impacts overall health
- Combined lifestyle factors can decrease life expectancy by up to 5.8 years
Obesity and Physical Activity
Obesity is a big challenge to longevity. For men, it shortens life by 1.3 years. For women, it’s 1.2 years.
Being active is linked to better health. It shows how important it is to stay active.
“Your lifestyle choices today determine your health outcomes tomorrow.”
Dietary Habits and Nutrition
Nutrition is crucial in managing chronic diseases. European diets, like the Mediterranean diet, are beneficial. Eating well can help counteract some lifestyle negatives.
By changing lifestyle habits, people can improve their longevity and health.
Socioeconomic Influences on Longevity Projections
The complex landscape of European demographics shows deep links between socioeconomic factors and life expectancy. Research shows that income, education, and social equality greatly affect how long people live in different European areas.
“Socioeconomic conditions are the silent architects of life expectancy trends”
Important socioeconomic factors that shape aging population dynamics include:
- Gross National Income (GNI) per capita
- Mean years of schooling
- Healthcare accessibility
- Employment stability
Statistical analysis gives us key insights into life expectancy. Countries with higher GDP per capita tend to have longer life expectancy. Places that see big improvements in their economy also see big increases in how long people live.
The link between economic growth and health outcomes is clear. Improved living standards lead to better healthcare, which means people live longer in Europe.
Mortality forecasts highlight the need for focused health policies. Despite progress, social and economic gaps still hinder health improvements. This calls for targeted efforts to tackle these inequalities.
Conclusion
The landscape of longevity trends in Europe shows a remarkable increase in life expectancy. By 2065, women are expected to live up to 92.8 years, and men to 90.5 years. This is a big jump from the 2014 baseline of 83.4 years for women and 78.3 years for men.
Research from the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research shows a steady increase in life expectancy. It takes into account important lifestyle factors like smoking, obesity, and alcohol. The Netherlands is expected to see life expectancy reach 93.2 years for women and 91.1 years for men by 2065. This is much higher than previous forecasts.
Across Europe, life expectancy varies, showing the complexity of the issue. While some countries are doing well, others face challenges. Healthcare, lifestyle choices, and socioeconomic factors will keep shaping life expectancy.
As European societies deal with these changes, policymakers and healthcare professionals need new strategies. The trends offer both chances and challenges. They require a detailed approach to healthcare, social support, and economic planning.
FAQ
What are the key factors influencing life expectancy projections in Europe for 2025?
Several factors are at play. These include better healthcare, lifestyle changes, and economic growth. Public health efforts and social conditions also matter. The COVID-19 pandemic’s effects are still being felt.
Healthcare quality and lifestyle choices are key. They affect how long people live in different European countries.
How has the COVID-19 pandemic affected life expectancy projections in Europe?
The pandemic has lowered life expectancy temporarily. It has made old projections seem too high. Countries have seen different impacts, with some facing bigger drops in life expectancy.
This has led to a review of healthcare and public health strategies. It’s a big challenge for Europe.
Are there significant regional differences in life expectancy across Europe?
Yes, there are big differences. Western Europe tends to have higher life expectancy. This is due to better economies, healthcare, and lifestyles.
Eastern Europe faces challenges. Countries like Switzerland and Spain have higher life expectancy. This shows the impact of lifestyle and healthcare.
What is the current gender gap in life expectancy in Europe?
Women generally live longer than men. The gap is 4-7 years. This is due to biology, lifestyle, and health choices.
Women tend to make healthier choices. They also get better healthcare. This helps them live longer.
How do lifestyle factors impact life expectancy projections?
Lifestyle choices are very important. Smoking, drinking, obesity, exercise, and diet all matter. Healthier habits lead to longer life.
Places that eat well, like those following the Mediterranean diet, see better life expectancy. Health campaigns are key to improving longevity.
What challenges do healthcare systems face in addressing increasing life expectancy?
Healthcare faces many challenges. It must care for more older people. It needs to improve prevention and manage chronic diseases.
It also needs to be affordable. This includes pensions and care for the elderly. Quality of life is crucial.
How do socioeconomic factors influence life expectancy in Europe?
Income, education, and employment affect life expectancy. Better education and income mean better health. This leads to a longer life.
Economic differences cause big gaps in life expectancy. This is seen in different social groups and regions.
What role do healthcare innovations play in improving life expectancy?
New healthcare technologies are vital. They help in prevention, early detection, and treatment. This improves life expectancy.
Technologies like precision medicine are becoming more important. They will help extend life even more in the future.
Source Links
- Europe Life Expectancy 1950-2025
- Mortality and life expectancy statistics
- Life Expectancy by Country and in the World (2025)
- Future life expectancy in Europe taking into account the impact of smoking, obesity, and alcohol
- Life Expectancy
- Where in Europe do people live the longest?
- Life Expectancy in Europe 1950-2025 & Future Projections
- 2024: the United Nations publishes new world population projections
- Europe Infant Mortality Rate 1950-2025
- Healthy life years statistics – Statistics Explained
- Gender equality related to gender differences in life expectancy across the globe gender equality and life expectancy
- Patterns in age and cause of death contribution to the sex gap in life expectancy: a comparison among ten countries – Genus
- Inequalities in regional excess mortality and life expectancy during the COVID-19 pandemic in Europe – Scientific Reports
- Stagnating mortality convergence across European regions in recent years – N-IUSSP
- Eurostat
- The Influence of Universal Health Coverage on Life Expectancy at Birth (LEAB) and Healthy Life Expectancy (HALE): A Multi-Country Cross-Sectional Study
- Risky Behaviours and Life Expectancy in Europe
- Healthy life expectancy for 202 countries up to 2030: Projections with a Bayesian model ensemble
- Projections of healthy working life expectancy in England to the year 2035 – Nature Aging
- Impact of Socio-Health Factors on Life Expectancy in the Low and Lower Middle Income Countries
- Socioeconomic development and life expectancy relationship: evidence from the EU accession candidate countries – Genus
- Higher future life expectancy values in Europe than previously forecasted – NIDI
- How bad are life expectancy trends across the UK, and what would it take to get back to previous trends?