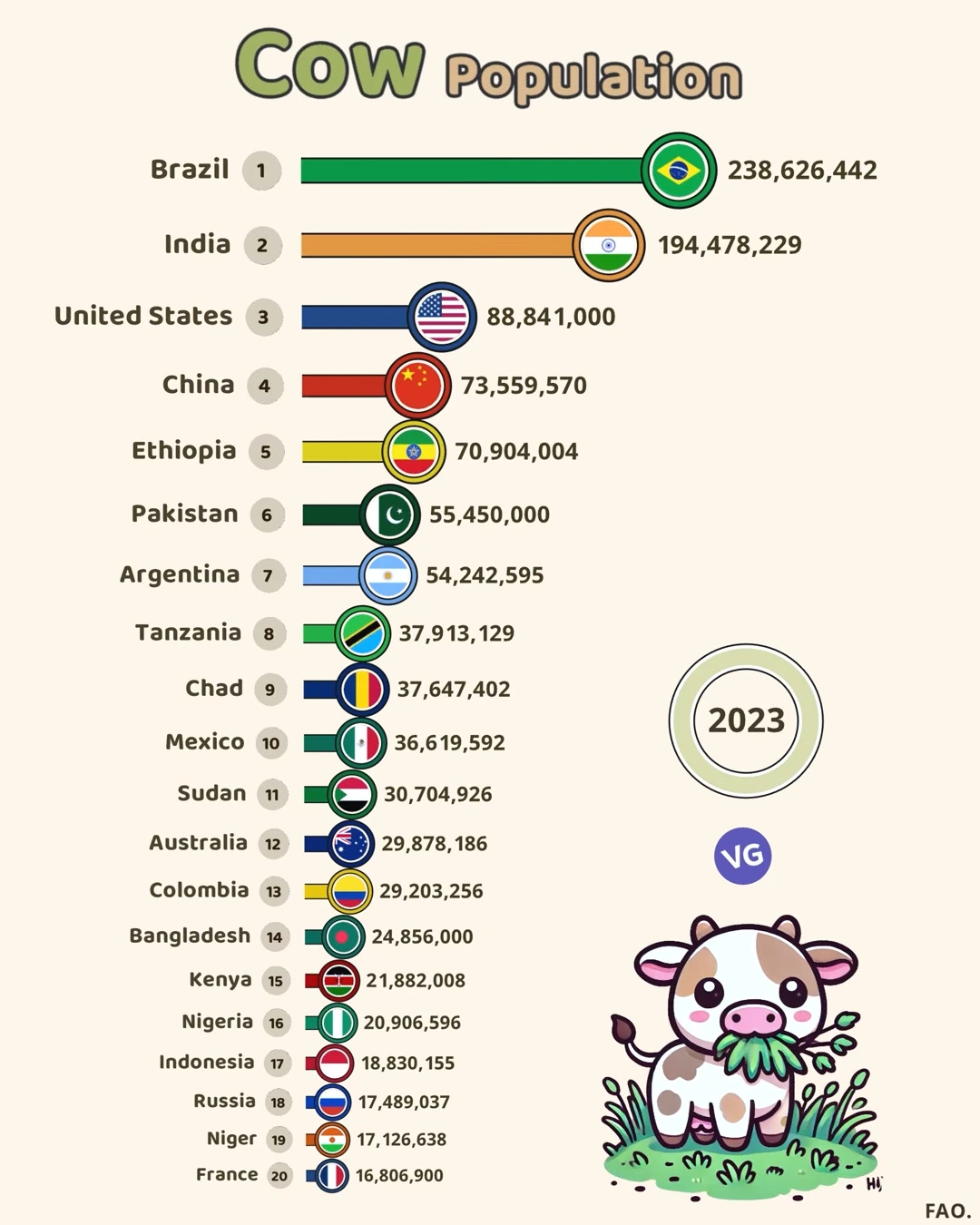
Our planet is home to over 940 million cattle. Some countries stand out as major players in the global cattle population. Brazil leads the way, with more than 230 million cows. It is the world’s largest beef cattle producer, according to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).
| Rank | Country | Flag | Cow Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brazil | 🇧🇷 | 238,626,442 |
| 2 | India | 🇮🇳 | 194,478,229 |
| 3 | United States | 🇺🇸 | 88,841,000 |
| 4 | China | 🇨🇳 | 73,559,570 |
| 5 | Ethiopia | 🇪🇹 | 70,904,004 |
| 6 | Pakistan | 🇵🇰 | 55,450,000 |
| 7 | Argentina | 🇦🇷 | 54,242,595 |
| 8 | Tanzania | 🇹🇿 | 37,913,129 |
| 9 | Chad | 🇹🇩 | 37,647,402 |
| 10 | Mexico | 🇲🇽 | 36,619,592 |
| 11 | Sudan | 🇸🇩 | 30,704,926 |
| 12 | Australia | 🇦🇺 | 29,878,186 |
| 13 | Colombia | 🇨🇴 | 29,203,256 |
| 14 | Bangladesh | 🇧🇩 | 24,856,000 |
| 15 | Kenya | 🇰🇪 | 21,882,008 |
| 16 | Nigeria | 🇳🇬 | 20,906,596 |
| 17 | Indonesia | 🇮🇩 | 18,830,155 |
| 18 | Russia | 🇷🇺 | 17,489,037 |
| 19 | Niger | 🇳🇪 | 17,126,638 |
| 20 | France | 🇫🇷 | 16,806,900 |
The global livestock statistics show a complex picture of agricultural production. The top cattle-producing nations are key to world food security, economic stability, and environmental balance. It’s crucial to understand the global cattle population as agricultural systems face new challenges.
Cattle are more than just farm animals. They symbolize economic strength, cultural heritage, and sustainable food production. These animals shape our global agricultural ecosystem.
Key Takeaways
- Brazil leads global cattle production with 230 million cows
- Global cattle population exceeds 940 million animals
- Cattle industries significantly impact economic and environmental landscapes
- Agricultural production varies widely across different countries
- Livestock statistics reflect complex global agricultural systems
Global Overview of Cattle Distribution
The global cattle industry is complex and dynamic. It spans many continents and economic systems. It shows us how livestock and agriculture work around the world.
Understanding Global Cattle Population
Cattle breeds vary greatly, fitting different climates and farming areas. The global cattle population shows big differences across continents:
- Taurine cattle are common in Europe and North America.
- Zebu cattle do well in warm and hot places.
- Sanga cattle are found in Africa’s farms.
Economic Impact of Cattle Industry
The livestock economy is very important worldwide. In the United States, cattle farming is a big part of agriculture. Here are some key numbers for 2022:
- Total cattle and calf production was $61.9 billion.
- Commercial beef production was 28.3 billion pounds.
- Beef exports were 3.5 billion pounds, worth $10.9 billion.
Factors Affecting Cattle Distribution
Many things affect where cattle are farmed. These include climate, land use, and policies. Important factors are:
- Climate and what plants grow there.
- Government rules and farm help.
- Support for beef farming.
- Old farming ways and culture.
“Cattle distribution is not just about geography, but a complex interplay of environmental, economic, and cultural dynamics.”
Knowing these complex relationships helps us understand the future of the global cattle industry.
d economy worldwide.
Major Cattle Production Systems Worldwide
Cattle farming varies a lot around the world. This is because of different landscapes and economic needs. The United States is a leader in advanced livestock management. It uses various systems that aim for both high production and sustainability.
There are three main types of modern cattle production systems:
- Intensive Feedlot Systems
- Extensive Grazing Systems
- Regenerative Farming Practices
In the United States, large-scale feedlots are common for raising cattle. Feedlots with 1,000 head or more account for less than 5% of operations but sell 80-85% of fed cattle. These places help cattle grow fast, gaining 2.5 to 4 pounds daily. They use special diets to help with this.
“The future of cattle farming lies in balancing productivity with environmental stewardship” – Agricultural Research Experts
On the other hand, countries like Argentina and Australia use extensive grazing systems. These methods focus on animal care and fitting into natural ecosystems. Cattle get to roam and eat native plants.
| Production System | Key Characteristics | Global Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Intensive Feedlots | High-density, controlled feeding | Common in USA, Canada |
| Pastoral Grazing | Large land areas, natural forage | Prevalent in South America, Australia |
| Regenerative Farming | Ecosystem-focused, sustainable practices | Growing globally |
New trends in cattle farming are all about using technology. Precision agriculture, genetic advancements, and data management are changing old ways. These changes help make farming more efficient and kinder to the environment.
Conclusion
Global livestock trends show big changes in the cattle industry. The United States has the lowest cattle number since 1951, with 87.2 million in 2024. This highlights the challenges in making beef production sustainable.
Agriculture worldwide faces tough economic and environmental issues. These need new solutions. The cattle industry must adapt to changing consumer wants and new technologies.
Climate change, new food choices, and money issues are changing how we raise cattle. Farmers need to find ways to be productive while taking care of the environment. They should look into better breeding and farming methods.
New technology in cattle farming is promising. It includes better genetics and nutrition. This tech could make farming more efficient and help feed more people without harming the planet.
To succeed, cattle farmers must balance making money with caring for the environment. The future requires being flexible, creative, and committed to better farming. This will help feed a growing world.
FAQ
What are the top countries with the largest cattle populations in 2023?
Brazil, India, China, the United States, and Argentina have the most cattle. Each country’s large herds come from different factors. These include agricultural policies, land, and economic plans for beef and dairy.
How does climate change impact global cattle distribution?
Climate change is changing where cattle are raised. Farmers must now adapt and move herds. They also choose breeds that can handle new weather patterns.
What are the main differences between cattle production systems?
There are two main ways to raise cattle: intensive farming and extensive grazing. Intensive farming uses feedlots, while grazing is more common in places like Argentina. Each method affects land, productivity, and animal welfare differently.
What types of cattle breeds exist globally?
There are taurine, zebu, and sanga cattle. Each is suited to different climates and places. This affects where they are found around the world.
How do cattle contribute to national economies?
Cattle help economies through beef, dairy, leather, and exports. They also support rural jobs and income. This is especially true for countries that rely on agriculture.
What emerging trends are shaping the global cattle industry?
New trends include organic farming and regenerative grazing. There’s also a focus on sustainable and ethical farming. These changes meet environmental needs and changing consumer tastes.
How are technological innovations impacting cattle farming?
New tech like genetic tracking and health sensors is changing farming. It helps manage herds better and improves animal care. This tech also boosts productivity.
What challenges does the global cattle industry face?
The industry faces many challenges. These include environmental issues, climate change, and rising costs. There’s also competition from other protein sources. Balancing profit with sustainability is a big challenge.
Source Links
- Meet the world’s most expensive cow
- A harmonized data set of ruminant livestock presence and grazing data for the European Union and neighbouring countries – Scientific Data
- Cattle & Beef – Statistics & Information
- World Beef Trade
- UK and EU cow numbers
- Cattle Population by Country 2024
- Agricultural production – livestock and meat
- Cattle & Beef – Sector at a Glance
- Cattle
- U.S. Cattle Inventory Smallest in 73 years
- Clustering of countries based on dairy productivity characteristics of Holstein cattle for breeding material selection
- Livestock Market Update for The Second Half of 2024