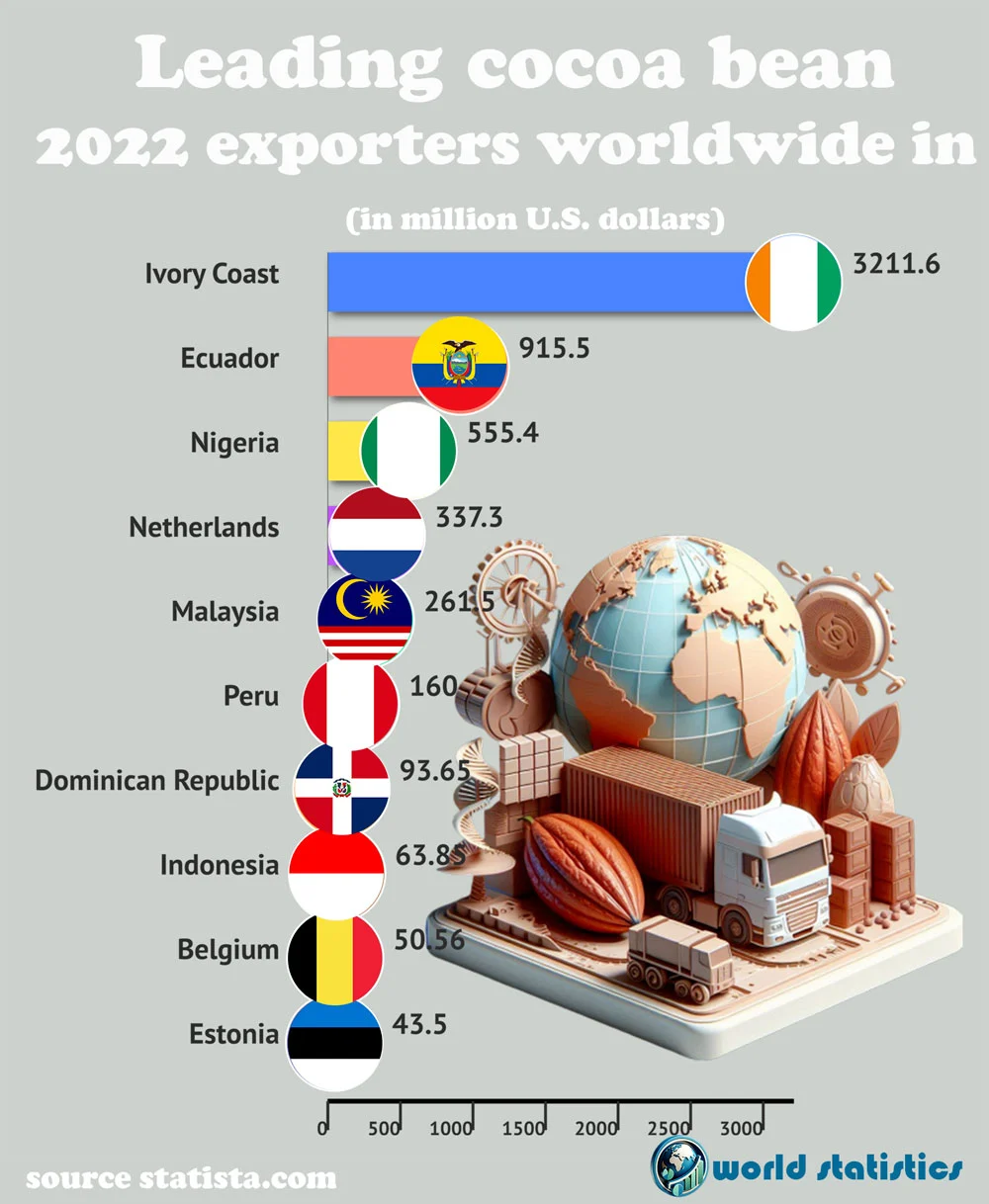
Surprisingly, only a few countries dominate the chocolate scene globally. In 2022, Côte d’Ivoire was the top exporter with $4.29 billion. Ghana followed with $1.37 billion, then came Ecuador at $819 million, Nigeria at $560 million, and Cameroon with $482 million1. They heavily influence how chocolate is made worldwide because of their large cocoa exports.
| Rank | Country | Flag | Export Value (million USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ivory Coast | 🇨🇮 | 3,211.6 |
| 2 | Ecuador | 🇪🇨 | 915.5 |
| 3 | Nigeria | 🇳🇬 | 555.4 |
| 4 | Netherlands | 🇳🇱 | 337.3 |
| 5 | Malaysia | 🇲🇾 | 261.5 |
| 6 | Peru | 🇵🇪 | 160.0 |
| 7 | Dominican Republic | 🇩🇴 | 93.65 |
| 8 | Indonesia | 🇮🇩 | 63.85 |
| 9 | Belgium | 🇧🇪 | 50.56 |
| 10 | Estonia | 🇪🇪 | 43.5 |
The cocoa business is worth billions, with these nations leading the way. Knowing about the top cocoa exporters helps us understand where the chocolate market is heading. This piece will look at how these countries export, their challenges in production, and what they’re doing for sustainability.
Key Takeaways
- Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Ecuador, Nigeria, and Cameroon are the world’s largest cocoa exporters.
- Côte d’Ivoire is the undisputed global leader, accounting for over 40% of the world’s cocoa production.
- Cocoa exports are a significant contributor to the economies of these top producing nations.
- Sustainability and ethical practices in the cocoa industry are increasingly important concerns.
- Emerging producers like Brazil and Peru are also making their mark in the global cocoa trade.
Introduction to the Global Cocoa Trade
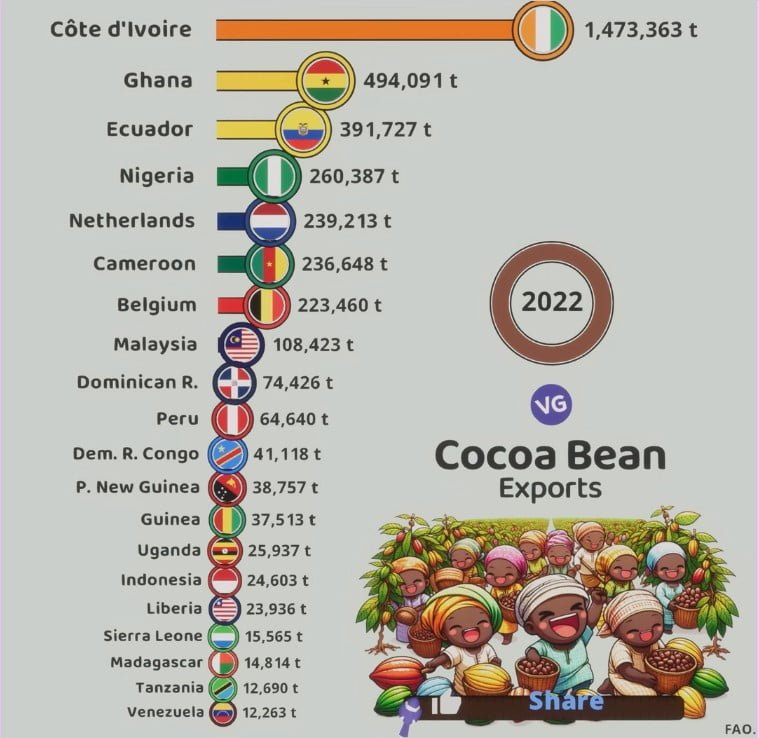
Cocoa Bean Exports (2022)
Source: International Cocoa Organization (ICCO)
The global cocoa trade plays a big part in the chocolate industry worldwide. Cocoa beans come from many countries and are a key part of making chocolate2. Knowing how the international cocoa market works helps us understand how much cocoa we need and want worldwide3.
A few countries lead in growing and selling cocoa beans3. These include Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Ecuador, Nigeria, and Cameroon. Together, they make up 85% of cocoa trade. Most cocoa beans come from Africa, about 77% of them3.
Some countries, like The Netherlands and Germany, buy a lot of cocoa beans3. Europe is the biggest importer, taking in 58% of all cocoa beans. North and Latin America take 25%, and Asia takes 17%4.
The market for cocoa beans has been growing4. In 2023, it was worth USD 16 billion. Experts say by 2028, it will be over USD 22 billion. That’s an increase of almost 7% every year. The chocolate market as a whole is also expected to grow by 4.4% yearly until 20304.
“Cocoa is the largest source of export earnings in Cote d’Ivoire, accounting for over 37% of total exports in 2015.”2
The cocoa industry faces issues like deforestation, child labor, and worker’s rights2. Producers, exporters, and consumers need to work together to solve these issues. It’s important for the future of cocoa trade.
With the cocoa market always changing, knowing the latest trends is key. This knowledge is important for everyone involved, from companies to governments, and us as consumers342.
Top Cocoa Exporting Countries in the World
A few countries lead in cocoa exports around the world. Mainly, Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana top the list. They are located in West Africa.
Côte d’Ivoire: The Undisputed Leader
In 2021, Côte d’Ivoire sent out cocoa worth $4.29 billion. It kept its spot as the top cocoa seller567. This amount was 60% of the world’s cocoa. So, it really rules the cocoa industry.
Ghana: A Close Second
Also in 2021, Ghana earned $1.37 billion from cocoa sales. This makes it second only to Côte d’Ivoire567. Its cocoa helps meet 20% of the world’s need. Ghana is a big player in cocoa trade.
Countries like Ecuador, Belgium, and more also add to the cocoa market567. These, along with Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana, make up 80% of the world’s cocoa sales. They are vital in the industry.
“The success of Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana in the global cocoa trade can be attributed to their favorable climatic conditions, rich soil, and long-standing traditions in cocoa cultivation.”
These leading cocoa countries greatly influence the global chocolate scene. They determine cocoa’s availability and cost worldwide.
The Importance of Cocoa Exports
Cocoa exports are key for the top cocoa-producing countries8. The Dominican Republic is a standout, selling US$261 million in 2015. It led in organic cocoa exports, with 60% of the market8. Over the past ten years, its cocoa exports grew by 322%8. Now, the country looks to double its exports within the next decade to hit US$500 million yearly8.
This sector offers many jobs, brings in a lot of money, and boosts these countries’ growth9. For example, in Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana, nearly 600,000 and over 3.2 million people work in cocoa9. Yet, small farmers make about $2 per day, presenting a big challenge9.
Moreover, cocoa exports are vital for making chocolate worldwide10. From 2000 to 2014, cocoa bean production grew by 32%. This jump showed the growing need for cocoa10. In 2014 alone, Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana earned $5.6 billion and $3.1 billion from cocoa sales, showing its huge economic impact10.
| Country | Cocoa Export Value (2014) |
|---|---|
| Côte d’Ivoire | $5.6 billion |
| Ghana | $3.1 billion |
Cocoa had a notable share of global land use and crop exports in 201410. It accounted for 0.7% of all the land used for crops and 1.5% of their exports. Then, in the main cocoa countries, cocoa took up 5% of agricultural land use and 9% of export trade10.
The cocoa sector also impacts the environment9. It generates around 700,000 tons of waste per year. Plus, 40% of Côte d’Ivoire’s cocoa is grown where it shouldn’t be, harming nature9. But, there are steps to tackle this, like a power plant in Côte d’Ivoire using cocoa waste for power9.
“Cocoa exports are the backbone of the economies of many developing countries, providing jobs, income, and economic development. As the world’s demand for chocolate continues to grow, the importance of this industry will only increase.”
So, cocoa exports are very important for many countries, offering jobs and growth. With a rising demand for chocolate, the cocoa trade will grow in significance. This underlines the need for sustainable and ethical ways in the cocoa business8910.
Factors Influencing Cocoa Production and Exports
The cocoa trade worldwide is affected by many things. These include the weather, the type of soil, how workers are treated, and efforts to ensure trade is fair11. These aspects are key in how much cocoa is grown and sold.
Climate and Soil Conditions
For cocoa to grow well, it needs the right mix of heat, rain, and fertile soil11. Cote d’Ivoire leads in growing cocoa, with over 70% of its exports being cocoa11. Ghana is also a big producer. These countries have perfect conditions for cocoa farming.
Labor Practices and Fair Trade Initiatives
Issues like using child labor and paying workers fairly are now big concerns in the cocoa business11. More than a million workers in Cote d’Ivoire depend on cocoa for their living11. To help, there are now fair trade plans. They work to ensure cocoa is grown in ways that are both good for the earth and the people who grow it.
Even in smaller countries like Ecuador, independent farmers are vital to cocoa production12. Most of their cocoa is sold to the US and EU. Ecuador also focuses on a special kind of cocoa, aiming to grow its market share12.
Indonesia, a key cocoa producer, is working hard to improve13. They’re focusing on better seeds, eco-friendly fertilizers, more support for farmers, and including women more in farming. All these efforts aim to raise cocoa farming’s success13.
How the climate works, how workers are treated, and the plans in place all shape the cocoa world. This affects how much cocoa is made and sold, and thus, the lives of many cocoa farmers everywhere111213.
The Largest Cocoa Exporters in the World
A few countries rule the global cocoa market, with Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana at the top14. Together, they make 60% of the world’s cocoa, producing over 4.9 million tonnes14.
Ecuador comes next, adding 9% to global cocoa stocks14. Indonesia, in Asia, is also a big player14.
| Country | Cocoa Production (Tonnes) | Global Market Share |
|---|---|---|
| Côte d’Ivoire | 2,230,000 | 45.5% |
| Ghana | 1,108,663 | 22.6% |
| Indonesia | 667,296 | 13.6% |
| Ecuador | 337,149 | 6.9% |
| Cameroon | 300,000 | 6.1% |
Most cocoa beans, up to 95%, are sold globally14. Europe processes a third of the world’s cocoa every year14. The Netherlands turns about 628,000 tons of beans annually14. Switzerland processes 53,000 tons, which is 1% of the world’s cocoa14.
In export value, Ghana is in the lead, selling $1.89 billion of beans in 20165. This is 39% of the global market’s share5. Ecuador is second, with $621 million in bean exports in 20165. Belgium, the Netherlands, and Malaysia also make up the top five, with 80% of the world market5.
In 2022, Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, and Ecuador showed huge cocoa production numbers6. Côte d’Ivoire made 2,230,000 tons6, Ghana 1,108,663 tons6, and Ecuador 337,149 tons6. Cameroon, Nigeria, Brazil, and Peru also have vital roles6.
“The cocoa industry is a complex web of production, trade, and processing, with a handful of countries dominating the global stage. Understanding the dynamics of the largest cocoa exporters is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and consumers alike.”
Emerging Cocoa Exporting Countries
Some countries like Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana have long been big in the world’s cocoa trade. But now, other nations are starting to shine6. Places like Ecuador, Nigeria, and Cameroon are adding to the cocoa supply. This creates new chances for the cocoa industry.
Ecuador is one of the new stars, shipping out 337,149 tons in 2022. Nigeria and Cameroon are also making a big impact by adding 280,000 tons and 300,000 tons, respectively6. These countries show how the world’s cocoa map is changing.
Places south like Brazil and Peru are also becoming important in cocoa, producing 273,873 tons and 171,177 tons in 20226. The Dominican Republic and Mexico are finding their own spaces too, adding 75,900 tons and 28,115 tons to the cocoa market6.
These countries aren’t just changing where cocoa comes from. They’re also bringing new ideas for how cocoa should be grown and traded. With cocoa demand growing, their role is becoming more significant every day6.
“The rise of these new cocoa-producing nations shows cocoa’s industry can overcome. They are vital for a cocoa trade that’s both fair and lasting, especially in the future.”
Sustainability and Ethical Concerns
The cocoa industry is facing big challenges. We’re focusing on making cocoa production sustainable and dealing with ethical issues. Most of the world’s cocoa comes from Western African countries like Ghana and the Ivory Coast, making up over 70%15. This huge demand is causing problems for the environment and the people there.
Deforestation and Environmental Impact
Cocoa farms are growing, but this means forests are being cut down in West Africa. Over the past 20 years, the land lost to cocoa farms has gone up by 62%15. This is bad for the environment. It messes up ecosystems and adds to climate change.
More people in the Asia Pacific are starting to eat chocolate, with consumption going up 3.2% in recent years15. This is making the situation worse for cocoa production and the environment.
Child Labor and Workers’ Rights
Child labor is a major issue in cocoa farming, with almost 2 million kids working on cocoa farms under dangerous conditions in Ivory Coast and Ghana15. People worldwide are speaking out against this bad practice. They are worried about the workers’ and children’s rights.
Small farmers in these areas don’t get a fair share of the $100 billion the chocolate industry makes16. More than half of Ivory Coast’s cocoa farmers live below the global poverty line because of this16. This shows we need better pay for these important farmers who grow cocoa and are directly affected by the impact of cocoa farming.

Fair trade programs like Fairtrade and Rainforest Alliance are trying to help. They focus on making cocoa farming better for the environment and fair for farmers16. But, there’s still work to do. Many think these programs should do more to really help the farmers16.
The world wants more chocolate, but we need to make sure it’s grown and made the right way. The cocoa industry has to work hard to solve the sustainability and ethical issues. This way, everyone involved can have a better future151617.
The Future of the Cocoa Industry
The demand for chocolate is growing around the world. For the cocoa industry, this means new challenges and chances ahead18. Every year, nearly 6 million tonnes of cocoa beans are produced globally. Most of this comes from West Africa. The Ivory Coast alone makes about 38% of the beans. Ghana adds another 19%, almost reaching 60% of what the world eats18.
Making cocoa farming sustainable and fair, as we meet the rising need for chocolate, is key for success in the future18. This year, global cocoa production might fall by up to half a million tonnes, a 10% drop. In the two top cocoa-producing countries, Ghana and the Ivory Coast, farmers are paid a fixed amount for their cocoa. But, the global price is much higher18.
New technology, better farming methods, and teamwork between all involved will decide where the cocoa industry goes next19. Cocoa prices are at their highest in years because there’s not enough cocoa to go around. This could mean chocolate prices will go up19. To make up for higher cocoa costs, some companies are thinking of raising chocolate prices. But, they have to be careful not to lose customers19.
The European Union is getting ready to stop buying cocoa from areas recently cleared of forests18. This could hit West African farmers hard since they sell a lot of cocoa to Europe. These new rules, along with other green and fair efforts, will really shape where the cocoa industry is going20. Between 1998 and 2010, cocoa production worldwide went up by 2.2% every year, hitting 3.7 million tonnes20. But, Africa’s part in this production is expected to drop just a little by 201020.
As the cocoa world faces these tests and chances, how well it handles being green, fair, and in demand decides its future. Côte d’Ivoire is forecasted to grow its cocoa production to 1.6 million tonnes yearly by 2010, making 44% of the world’s cocoa.
“The future of the cocoa industry will be defined by our ability to balance sustainability, ethical practices, and the growing global demand for chocolate.”
By being open to new ideas, working together, and putting the planet first, the cocoa industry can make a better world for everyone who loves chocolate.
Conclusion
Cocoa comes mainly from a few countries. Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana are the top producers and exporters21. They make over half the world’s cocoa. These two countries earned around US$7 billion together in 2019/202022.
But, there are big challenges in the cocoa industry. Small family farms are at risk. There are also worries about cutting down trees and child labor2322.
The world wants more chocolate. By 2025, the chocolate market could hit US$186 billion22. It’s urgent to make cocoa farming sustainable and fair. This means fixing old farming ways and planting new kinds of cocoa in countries like Nigeria and Indonesia2123.
The cocoa business needs to change for the better. This change depends on governments, farmers, and chocolate makers working together. They need to focus on helping small farmers, fairness, and the environment2322. Then, we can have good cocoa and do good for people and the planet.
FAQ
What are the leading cocoa bean exporters worldwide in 2022?
Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, and Ecuador topped the list for cocoa bean exports in 2022. They were followed by Nigeria and Cameroon. In total, they brought in billions of dollars from their cocoa trades.
What is the role of cocoa exports in the global chocolate industry?
Cocoa exports are super important for making chocolate. They make sure there’s enough raw cocoa for chocolate bars across the world.
Why are Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana considered the world’s top cocoa exporters?
Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana are the top exporters because they sell huge amounts of cocoa. In 2021 alone, Côte d’Ivoire sold .29 billion worth, and Ghana sold
FAQ
What are the leading cocoa bean exporters worldwide in 2022?
Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, and Ecuador topped the list for cocoa bean exports in 2022. They were followed by Nigeria and Cameroon. In total, they brought in billions of dollars from their cocoa trades.
What is the role of cocoa exports in the global chocolate industry?
Cocoa exports are super important for making chocolate. They make sure there’s enough raw cocoa for chocolate bars across the world.
Why are Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana considered the world’s top cocoa exporters?
Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana are the top exporters because they sell huge amounts of cocoa. In 2021 alone, Côte d’Ivoire sold $4.29 billion worth, and Ghana sold $1.37 billion. This makes them key players in the cocoa trade worldwide.
How important are cocoa exports for the economies of the leading cocoa-producing countries?
Cocoa exports are key for these countries. They provide many jobs, bring in a lot of money, and help the economies grow. The cocoa industry is very important for their economic success.
What factors influence cocoa production and exports?
Climate, soil, and farming practices affect how much cocoa a country can export. The right temperature, rainfall, and soil are needed for good cocoa. Fair labor practices are also critical today. They include ensuring workers receive fair wages.
What are some of the emerging cocoa exporting countries in the global market?
Some new countries are becoming cocoa exporters in a big way. These include Ecuador, Nigeria, and Cameroon. Although places like Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana still lead, these new countries are growing their share of the market.
What are the sustainability and ethical concerns in the cocoa industry?
There are big concerns about how cocoa production impacts the environment. Deforestation is a major problem. Cocoa production has also faced criticism for the use of child labor and unfair conditions for workers. These are pressing issues that need addressing.
.37 billion. This makes them key players in the cocoa trade worldwide.
How important are cocoa exports for the economies of the leading cocoa-producing countries?
Cocoa exports are key for these countries. They provide many jobs, bring in a lot of money, and help the economies grow. The cocoa industry is very important for their economic success.
What factors influence cocoa production and exports?
Climate, soil, and farming practices affect how much cocoa a country can export. The right temperature, rainfall, and soil are needed for good cocoa. Fair labor practices are also critical today. They include ensuring workers receive fair wages.
What are some of the emerging cocoa exporting countries in the global market?
Some new countries are becoming cocoa exporters in a big way. These include Ecuador, Nigeria, and Cameroon. Although places like Côte d’Ivoire and Ghana still lead, these new countries are growing their share of the market.
What are the sustainability and ethical concerns in the cocoa industry?
There are big concerns about how cocoa production impacts the environment. Deforestation is a major problem. Cocoa production has also faced criticism for the use of child labor and unfair conditions for workers. These are pressing issues that need addressing.
Source Links
- https://currentaffairs.adda247.com/top-10-cocoa-producing-countries-in-the-world/
- https://agrojournal.org/22/05-03.pdf
- https://www.spglobal.com/marketintelligence/en/mi/podcasts/ecr/ep-208-the-global-cocoa-trade.html
- https://www.cbi.eu/market-information/cocoa/what-demand
- https://www.worldatlas.com/articles/the-world-s-top-exporters-of-cocoa-beans.html
- https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/cocoa-producing-countries
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/top-10-cocoa-producing-countries-in-the-world/
- https://iica.int/es/prensa/noticias/cocoa-key-crop-keeps-dominican-republic-one-leading-countries-export-organic
- https://www.wri.org/insights/hidden-benefits-cacao-waste
- https://resourcetrade.earth/publications/cocoa-trade-climate-change-and-deforestation
- https://journalofeconomicstructures.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s40008-019-0135-5
- https://www.redalyc.org/journal/339/33968022006/html/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6448898/
- https://www.kakaoplattform.ch/about-cocoa/cocoa-facts-and-figures
- https://sourcetrace.com/blog/is-your-chocolate-ethical/
- https://www.ethicalconsumer.org/food-drink/shopping-guide/ethical-chocolate
- https://www.banqu.co/blog/sustainable-cocoa-deforestation-free
- https://www.sustainabilitybynumbers.com/p/cocoa-prices
- https://www.jpmorgan.com/insights/global-research/commodities/cocoa-prices
- https://www.fao.org/4/y5143e/y5143e0x.htm
- https://cluizel.us/blogs/michel-cluizel-chocolate-blog-spot/the-largest-cocoa-producers-in-the-world
- https://www.researchtecglobal.com/report/african-cocoa-production-market-analysis
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/cocoa-export-value-top-3-west-african-exporting-countries-makut