What makes a country truly prosperous? Is it the sheer size of its economy, or the wealth enjoyed by its citizens? As we explore the richest countries in Europe, we’ll uncover a fascinating blend of economic powerhouses and tiny-but-wealthy microstates. Each has its unique story of prosperity.
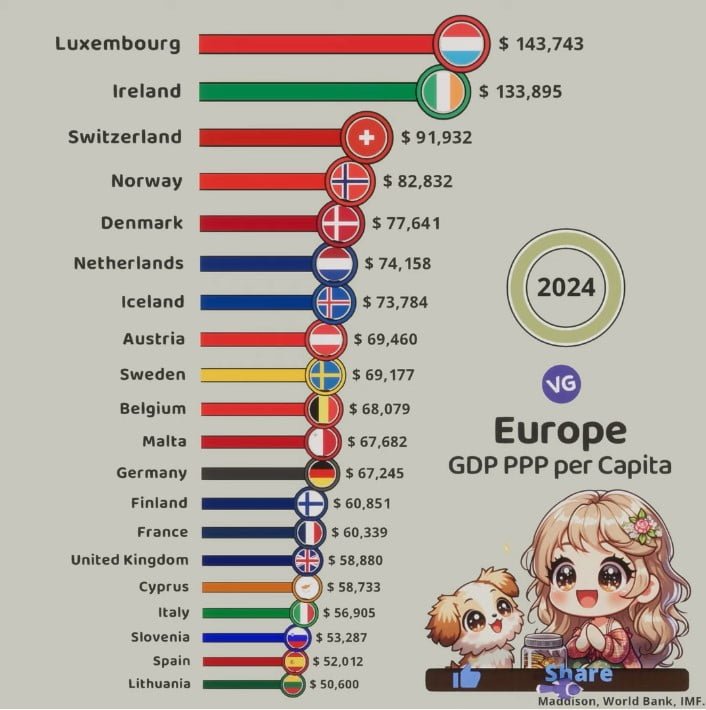
The Richest Countries in Europe GDP PPP per Capita
| Rank | Country | Flag | GDP PPP per Capita (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Luxembourg | 🇱🇺 | 143,743 |
| 2 | Ireland | 🇮🇪 | 133,895 |
| 3 | Switzerland | 🇨🇭 | 91,932 |
| 4 | Norway | 🇳🇴 | 82,832 |
| 5 | Denmark | 🇩🇰 | 77,641 |
| 6 | Netherlands | 🇳🇱 | 74,158 |
| 7 | Iceland | 🇮🇸 | 73,784 |
| 8 | Austria | 🇦🇹 | 69,460 |
| 9 | Sweden | 🇸🇪 | 69,177 |
| 10 | Belgium | 🇧🇪 | 68,079 |
| 11 | Malta | 🇲🇹 | 67,682 |
| 12 | Germany | 🇩🇪 | 67,245 |
| 13 | Finland | 🇫🇮 | 60,851 |
| 14 | France | 🇫🇷 | 60,339 |
| 15 | United Kingdom | 🇬🇧 | 58,880 |
| 16 | Cyprus | 🇨🇾 | 58,733 |
| 17 | Italy | 🇮🇹 | 56,905 |
| 18 | Slovenia | 🇸🇮 | 53,287 |
| 19 | Spain | 🇪🇸 | 52,012 |
| 20 | Lithuania | 🇱🇹 | 50,600 |
Europe is home to several of the world’s wealthiest nations. These countries have booming economies and high living standards.1 The most common way to measure a country’s wealth is through Gross Domestic Product (GDP). This figure represents the value of a nation’s goods and services in a year. The top six European countries each had a GDP over $1 trillion in 2020. Together, they reached a staggering $13.833 trillion. This shows how productive Europe’s leading nations are.
Learn more about a nation’s wealth by looking at GDP per capita and Gross National Income (GNI) per capita too.1 Monaco stands out as the richest when we look at GDP per capita. It earned $242,611 for every citizen. Liechtenstein and Luxembourg follow closely. Looking at GNI per capita, we see a similar trend, except Monaco switches places with Norway. Luxembourg and Switzerland still rank high.1
GDP per Capita (PPP) in European Countries
Source: World Bank, IMF (2024)
Key Takeaways
- Europe is home to some of the wealthiest countries in the world, with thriving economies and high living standards.
- The top six major European countries had a collective GDP of $13.833 trillion (US$) in 2020.
- GDP per capita and GNI per capita offer a more comprehensive view of a country’s wealth and prosperity.
- Monaco, Liechtenstein, and Luxembourg lead the list of the richest countries in Europe by GDP per capita.
- Norway, Luxembourg, and Switzerland are the top three European countries by GNI per capita.
Measuring Wealth: GDP and Beyond
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) shows a country’s wealth. It measures the value of goods and services produced in a certain time.2 Yet, it’s biased toward countries with more people. This is because it ignores the size of the workforce or the number of companies involved. So, for a fuller picture of how rich a nation is, economists look at GDP per capita and Gross National Income (GNI) per capita.
GDP per Capita
GDP per capita divides the GDP by how many people live in the country. This gives a better idea of the wealth of the average person in that country.3
Gross National Income (GNI)
GNI is the total value of money earned by a country’s products and services. This includes money coming in or going out with international trade.3 These ways to measure wealth give a broader look at a country’s economic success and quality of life.
Top European Economies by GDP
The1 top six major countries in Europe all had a GDP of over $1 trillion in 2020. Germany led with $4.59 trillion, the United Kingdom followed at $3.50 trillion, and France at $3.13 trillion.4 These figures placed Europe among the world’s most productive countries.
Germany
Germany shines with its strong industrial base and exports.5 With a GDP of $4,200,000 million, it stands at the top in Europe.4 In 2024, Germany’s GDP was $4,591.100 billion.
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom is a top financial center, with London as a key hub for global finance.4 It holds the second spot in Europe with a 2024 GDP of $3,495.261 billion.
France
France has a rich economy with strong sectors like aerospace and luxury goods.4 It ranks third in Europe with a 2024 GDP of $3,130.014 billion.
Wealthiest Countries by GDP per Capita
When we look at GDP per capita, three small places stand out. They are very rich for their size.
Monaco
tops the list with an impressive $242,611 GDP per capita.1followed by
Liechtenstein
at $194,816,1and
Luxembourg
at $123,234.1How do such small places get so wealthy? It’s partly because it’s easier to boost numbers with fewer people. Also, being known for low taxes draws business, which boosts their GDP in a big way.1Luxembourg’s money comes from a strong finance industry and friendly tax rules,1Switzerland makes a lot from its top-notch banking and medicine sectors.
Prosperity Drivers: Factors Behind Europe’s Wealthy Nations
The prosperity of Europe’s richest countries comes from several main reasons. One key aspect is how these places use their financial systems and tax rules. Countries like Luxembourg, Switzerland, and Ireland have made it easy for big global companies to set up there. This helps their economies to grow fast.6 These places have tax rules that attract companies to make their main offices or big parts of their businesses there.
Also, putting a big effort into new ideas and technology has helped these countries a lot. Their governments have spent a lot of money on research and new products. This is especially true for areas like finance technology, drugs, and clean energy. These efforts have created many well-paid jobs and have made their economies more varied.
Lastly, having a lot of natural resources and making energy has benefited some of Europe’s nations. For instance, Norway has lots of oil and gas. This has made their economy very strong.6 Besides oil, Norway also does well in things like shipping, making clean energy, and using new technologies.6 These things have altogether helped make Europe’s richest countries do so well.
The Richest Countries in Europe
According to the data, Luxembourg, Switzerland, and Norway are the top three richest countries in Europe.6 Luxembourg leads with a GDP per capita over $115,000, the world’s highest in 2022. It owes its wealth to a diverse economy that includes finance, steel, and telecommunications.
Switzerland follows, powered by its thriving banking and pharmaceutical industries.6 It also focuses on innovation and technology. Norway comes in third. Its wealth grew significantly in the late 1960s when it found massive oil reserves in the North Sea.
This discovery changed Norway’s economy. It started climbing the global wealth ladder quickly.6 The Government Pension Fund Global helped Norway wisely manage its oil money. This fund plays a big part in Norway’s ongoing prosperity.
High-Income European Economies
Europe has three top wealthy countries: Luxembourg, Switzerland, and Norway. There are also other high-income European economies. Ireland, Denmark, Iceland, Sweden, and the Netherlands count here, with over $50,000 GDP per capita.7 These prosperous European nations are known for their strong economies. They have diverse industries and high innovation. Their high living standards come from good financial setups, low taxes, and investments in education and tech.176 The wealth and success of these nations in Europe show the region’s strong economy. It also shows how they take care of their people and keep wealth growing.
| Country | GDP per Capita (2023 est.) |
|---|---|
| Luxembourg | $143,3047 |
| Ireland | $137,6387 |
| Switzerland | $89,5377 |
| San Marino | $84,1357 |
| Norway | $82,2647 |
| Denmark | $74,9587 |
| Netherlands | $73,3177 |
The success of these high-income European economies is a strong sign. It shows Europe’s economic strength and care for its people’s wealth and health.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Europe’s richest nations have seen big economic wins. Yet, they have challenges too. The big issue is the aging population. This shift can strain social and job systems, needing new policies to deal with it.
Aging Populations
Europe’s population getting older is a big worry for its economies.8 The EU’s jobless rate will rise to 6.2% in 2023 and 6.1% in 2024. It will pressure social and job systems as more people retire. Policymakers must cope with these changes to keep economies growing strong.
Environmental Sustainability
Staying green is vital for Europe’s top nations too.8 Gas and oil prices will drop in 2023 and 2024. This makes it key for them to switch to clean energy. They need to balance growing their economies with fighting climate change.
Global Competitiveness
Being competitive worldwide is always on their minds as well.9 Almost 2,900 bad trade actions have been taken. This includes tariffs and subsidies. Europe needs to stay sharp by focusing on education, tech, and being flexible in the market.
The challenges of aged populations, green goals, and staying global are key for Europe’s stronger economies to tackle. Their success in adapting and innovating will shape the region’s future prosperity.8 Private spending growth in the EU will be at 0.5% in 2023 and 1.8% in 2024. This underlines the importance of staying competitive and driving sustainable growth.
Europe’s Economic Powerhouses
Europe’s top economies include Germany, the United Kingdom, and France.5 Germany leads in manufacturing, especially in cars, machinery, and chemicals. These industries help it be a world leader.5 The United Kingdom shines in finance, with London as a global finance and banking hub.10 On the other hand, France thrives in many sectors, including aerospace, cars, luxury items, and farming. It also has a strong service sector.5 Together, these countries shape Europe’s economic future.
Germany’s Industrial Might
Germany dominates Europe economically with a $4.2 trillion GDP.5 It excels in manufacturing, highlighted by cars, machinery, and chemicals. This leadership comes from high tech and quality products in global demand.
United Kingdom’s Financial Hub
The United Kingdom stands out in finance, with London as a key financial and investment center.10 The financial sector boosts the UK’s income and job numbers. Also, its strong positions in regulation and big finance firms attract business globally.
France’s Diverse Economy
France is known for its wide economy, including aerospace, cars, luxury goods, and farming, plus strong service activities.5 This mix helps France stay strong during global economic troubles.10 Its focus on new ideas and industry keeps France a top European economy.
Wealth Distribution and Inequality
Europe has some very wealthy nations. But, the wealth and income aren’t spread equally.11 The top 10% in Europe own 67% of all wealth. Meanwhile, the bottom half has just 1.2%.11 In 2022, wealth inequality in Europe varied. It was from 50.8 in Slovakia to 87.4 in Sweden.11 Germany had a high wealth inequality score of 77.2 among the EU’s biggest economies.11
Sweden and Denmark do well in keeping income inequality low. They have strong welfare systems and policies for fairness.12 In 2022, the EU’s Gini coefficient for income was 29.6.12 Yet, 11 EU countries had more income inequality than the average.12 But, Spain and Greece struggle with wealth inequality, especially after the financial crisis.
Dealing with wealth inequality is crucial for European policymakers. They want to make sure everyone benefits from the economic growth.11 Places like Finland, Denmark, Norway, and Sweden still face high wealth inequality.11 In Sweden, the richest 10% own 74.4% of all wealth. The top 5% own 60.3%.11 Yet, Belgium has the lowest inequality, with the top 5% having 30.8% of wealth.11
Home ownership plays a big role in wealth distribution. In 2022, Germany had very low home ownership rates.11 Also, wealth inequality in Europe’s major countries has stayed the same or slightly improved. This is over the last 20 years.11
The Role of the European Union
The European Union greatly influences the economy across its member states. It’s made up of 27 countries. Together, they created a massive GDP of 14.45 trillion euros in 2021, equal to about US $15.49 trillion. This puts it as a key economic player worldwide.13
Economic Integration
The EU brings countries together economically. It encourages cooperation, the sharing of policies, and the free flow of goods, services, money, and people. This has increased trade among countries in a bloc. Before the EU, trade growth was at 3%. Now, it’s 1.5% faster within these groupings.9
Trade Policies
The EU’s trade rules have lifted member states’ economies. It granted them access to a huge market and simpler global trade. Yet, the EU is open to trade risks. For example, 40% of its imports come from countries not partnering with the EU. Plus, about half of these imports might be hard to get from other places.9
Shared Currency
13 Nineteen EU countries use the euro as their currency, known as the eurozone. This started on January 1, 1999. The euro helped make their economies more stable and integrated. But, it also caused challenges, like the European debt crisis. Some countries faced severe financial issues in 2010-2012, requiring help from the EU under strict rules.13
13 Balancing wealth and growth across the EU has been tough, especially with a common currency. Unlike the US, the EU doesn’t help as much with money transfers between its different regions.13
9 After Russia’s actions in Ukraine, the EU became less reliant on energy from outside. It dropped its direct imports of Russian gas from over 20% in 2020 to around 5% in the first half of 2023. Now, gas prices have doubled since then.9
Emerging European Economies
Besides the rich countries, Europe holds many emerging and developing economies. Places like5 Poland, the Czech Republic, Hungary, and Romania have grown a lot. This growth is due to things like foreign investments and becoming part of the EU, plus their work in making more goods and services.14 These places are not as rich as some others on the continent.
But, they are making progress. Their growing impact shows that Europe’s economic map may change. We could see new economic powerhouses rise in addition to the current leaders in the future.
The up-and-coming European nations face hard times but show they can bounce back.14 Forecasts say they will grow faster from 2023 to 2024, from 1.1% to 3%.14 This beats how well richer European nations are expected to do.
This shows Europe’s economy is always changing. Developing economies in Europe are moving up. They might change the order of Europe’s economies in the future.
Conclusion
Europe has a dynamic economy with various countries. It ranges from the rich microstates of Monaco and Liechtenstein to the powerful industrial nations such as Germany and the UK.6 This diversity in wealth comes from different factors. These include strong financial services, smart tax rules, and cutting-edge innovations. These countries also use their natural resources well.6 While the richer countries stay on top economically, Europe also has growing economies ready to expand. This shows that the region’s financial map might change more.
European nations face issues like getting older, protecting the environment, and staying competitive worldwide. How well they adjust and come up with new ideas will be key to their future wealth.6 Detailed stats15 underline Europe’s economic might and diversity. They show the continent’s important role as a leading global economic force.
In the future, Europe’s wealthiest nations615 will likely stay important. Their success stories could inspire other countries. Yet, their ability to meet new challenges and keep their competitive advantage is critical. This will influence Europe’s economy in the coming years.
FAQ
Which are the richest countries in Europe?
The data shows Luxembourg, Switzerland, and Norway as Europe’s wealthiest.
What factors contribute to the prosperity of Europe’s wealthiest nations?
Europe’s wealth comes from strong financial services and tax systems. Also, from innovations, technological advancements, and rich natural resources. Energy production plays a significant role too.
How do economists measure a country’s wealth beyond just GDP?
Economists look at GDP, GDP per capita, and GNI per capita. This helps them understand a country’s wealth and the people’s living standards better.
What are the economic powerhouses among European countries?
Germany, the United Kingdom, and France stand out as Europe’s economic leaders. They have diverse and impactful economies.
How does wealth distribution vary across Europe?
Europe holds many wealthy nations. Yet, the wealth and income aren’t equally spread. This leaves some countries struggling more with wealth inequality.
What role has the European Union played in shaping the economic landscape of Europe?
The EU boosts economic integration and aligns policies. It also makes international trade easier among its members. The EU has played a huge part in Europe’s economic success.
Are there any emerging or developing economies in Europe?
Indeed, Europe sees growth not only in high-income areas. Countries like Poland, the Czech Republic, Hungary, and Romania are developing rapidly. They’ve seen economic booms over the last few decades.
Source Links
- https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/richest-european-countries
- https://unsceb.org/sites/default/files/2023-01/Valuing What Counts – UN System-wide Contribution on Beyond GDP (advance unedited).pdf
- https://gfmag.com/data/richest-countries-in-the-world/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_sovereign_states_in_Europe_by_GDP_(nominal)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Financial_and_social_rankings_of_sovereign_states_in_Europe
- https://bestdiplomats.org/richest-countries-in-europe/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_sovereign_states_in_Europe_by_GDP_(PPP)_per_capita
- https://economy-finance.ec.europa.eu/economic-forecast-and-surveys/economic-forecasts/spring-2023-economic-forecast-improved-outlook-amid-persistent-challenges_en
- https://www.imf.org/en/News/Articles/2023/11/30/sp-fdmd-remarks-bernhard-harms-prize
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_Europe
- https://www.euronews.com/business/2024/04/01/wealth-inequality-where-in-europe-is-wealth-most-unfairly-distributed
- https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Living_conditions_in_Europe_-_income_distribution_and_income_inequality&oldid=528159
- https://www.investopedia.com/terms/e/europeanunion.asp
- https://finance.yahoo.com/news/25-richest-poorest-countries-europe-122851738.html
- https://gfmag.com/data/worlds-richest-and-poorest-countries/