The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has released new data. Zimbabwe has the highest inflation rate in the world in 2023 at a staggering 284.94%1. Venezuela is second with 210%2, and Sudan has an inflation rate of 154.91%12. The COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain issues, and the Russia-Ukraine war have caused global inflation to soar.
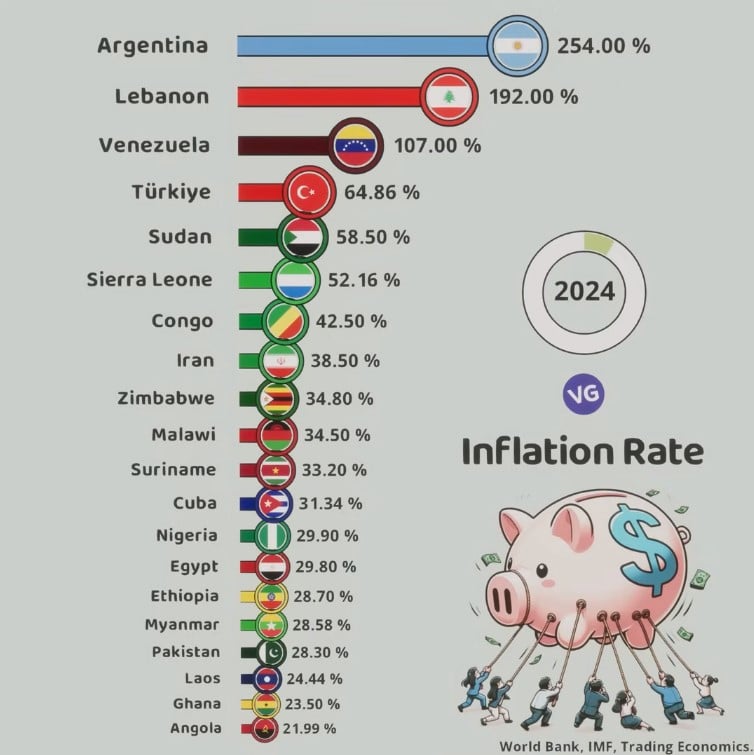
Inflation Rates in Various Countries (2024)
| Country | Inflation Rate | Flag |
|---|---|---|
| Argentina | 254.00% | 🇦🇷 |
| Lebanon | 192.00% | 🇱🇧 |
| Venezuela | 107.00% | 🇻🇪 |
| Türkiye (Turkey) | 64.86% | 🇹🇷 |
| Sudan | 58.50% | 🇸🇩 |
| Sierra Leone | 52.16% | 🇸🇱 |
| Congo | 42.50% | 🇨🇬 |
| Iran | 38.50% | 🇮🇷 |
| Zimbabwe | 34.80% | 🇿🇼 |
| Malawi | 34.50% | 🇲🇼 |
| Suriname | 33.20% | 🇸🇷 |
| Cuba | 31.34% | 🇨🇺 |
| Nigeria | 29.90% | 🇳🇬 |
| Egypt | 29.80% | 🇪🇬 |
| Ethiopia | 28.70% | 🇪🇹 |
| Myanmar | 28.58% | 🇲🇲 |
| Pakistan | 28.30% | 🇵🇰 |
| Laos | 24.44% | 🇱🇦 |
| Ghana | 23.50% | 🇬🇭 |
| Angola | 21.99% | 🇦🇴 |
Some countries are seeing a slowdown in inflation. But, many are still facing high inflation rates that are hurting their economies and reducing people’s buying power. This situation has led policymakers and economists to look for ways to lower living costs.
Key Takeaways
- Zimbabwe has the world’s highest inflation rate in 2023 at 284.94%, leading to significant financial challenges and soaring prices of essential goods and services.
- Venezuela follows with an inflation rate of 210%, indicating severe economic turmoil and widespread poverty.
- Sudan experiences an inflation rate of 154.91%, requiring attention to stabilize the economy and improve living conditions.
- Turkey faces an inflation rate of 73.13%, influenced by various factors such as currency fluctuations and external pressures.
- Several countries, including China, Switzerland, and the Netherlands, have relatively low inflation rates in 2023, ranging from -0.1% to 3.0%.
What is Inflation and Why Does it Matter?
Inflation Rates in Various Countries (2024)
Source: World Bank, IMF, Trading Economics (as shown in the image)
.
Inflation means prices go up over time in an economy3. It changes how much money you can buy. Things that cause inflation include more money being made, higher costs to make things, and problems in supply chains4. A little bit of inflation can help the economy grow. But too much can lower what you can buy, make people uncertain, and raise interest rates.
Definition and Causes of Inflation
Inflation is when prices go up over time3. It happens when there’s more money around, costs go up, or supply chains get disrupted4. When people want more goods and services than there are, prices go up.
Impact of Inflation on Economies and Individuals
Inflation can be good or bad for an economy4. A little bit can make people spend and invest more. But too much can make a currency almost worthless, like in Zimbabwe and Venezuela4. It also lowers what you can buy, making life harder and leading to trouble.
“Inflation is like riding a roller coaster. It can be exhilarating at first, but if it goes too high, it can cause a lot of economic damage.” – Expert Economist
In the U.S., inflation was 3% last year and 3.3% the latest month3. Without food and energy, it was 3.3%, up from 3.4% before3. The Federal Reserve wants inflation at 2%, but it’s up 20.8% since February 20203. The cost of living has gone up by 3% from last year3. The PCE index shows inflation at 2.6%3.
Inflation affects both the economy and people. Knowing about inflation helps policymakers, businesses, and consumers deal with the economy’s ups and downs4.
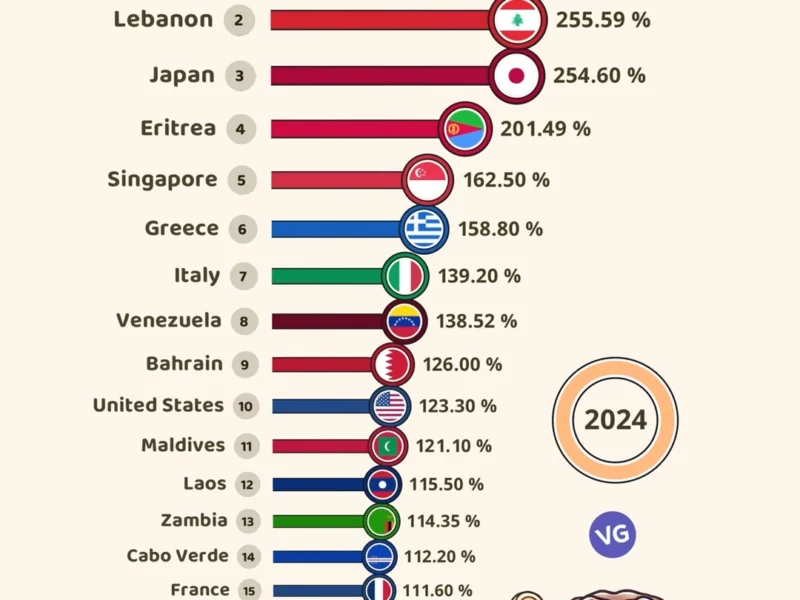
Countries with Soaring Inflation Rates in 2023
The global economy is facing a big rise in inflation. Many countries are seeing huge price jumps. Zimbabwe and Venezuela are among the worst hit, with their economies getting worse fast.
Zimbabwe: A Hyperinflationary Nightmare
Zimbabwe now has the highest inflation rate in the world, at 284.94% in 20235. This crisis comes from long economic troubles, political issues, bad management, and international sanctions. The Zimbabwean dollar’s value has dropped a lot, making life very hard for people.
Venezuela: The Ongoing Economic Collapse
Venezuela has the second-highest inflation rate, with prices up 210% in 20235. This is the tenth year in a row it’s among the top inflation countries. The cause is the country’s economic failure, due to poor management, corruption, and US sanctions.
In these countries, high inflation is causing big economic problems. It’s reducing people’s buying power and their standard of living6. The situation in Zimbabwe and Venezuela shows how bad inflation can be. It highlights the need for good economic policies and leadership.
“Hyperinflation is a situation where the price increases are so out of control that the currency becomes worthless.” –
Worst Inflation in the World 2023: Key Drivers and Factors
The global inflation in 2023 has seen a big jump. This is due to the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain issues, and the Russia-Ukraine war7. The pandemic made production drop in many areas, causing prices to go up. The war has also hit the global supply and prices of important items like food and energy7. Governments’ easy money policies and big spending to help their economies during the pandemic have added to the inflation in many places7.
Supply chain disruptions from the pandemic have been a big factor in inflation7. These disruptions have led to shortages of many goods and materials, making prices go up7. The Russia-Ukraine war has made things worse by disrupting the global supply of things like oil, gas, and grains, which has pushed up prices even more7.
Government actions to fight the pandemic have also played a big part in inflation7. These actions have increased the money in circulation, leading to higher demand and prices7. Also, people buying more goods instead of services during the pandemic has put more pressure on supply chains, adding to inflation8.
These factors have led to some of the highest inflation rates in years, with countries like Argentina, Turkey, and Venezuela seeing hyperinflation9. As leaders try to fix these issues, it’s clear that the main causes of inflation in 2023 will greatly affect economies and people worldwide7.
“The inflation surge has been driven by a complex interplay of supply and demand factors, exacerbated by global events like the pandemic and the war in Ukraine. Untangling these dynamics will be crucial for policymakers to bring inflation under control.”
Regional Trends: Inflation Hotspots Around the Globe
Many regions worldwide have seen the impact of rising prices. Africa stands out as a hotspot for high inflation, with some countries seeing among the highest rates10. On the other hand, Europe has generally kept inflation in check, but there are big differences across the region.
Africa: Political Instability and Economic Mismanagement
Africa’s high inflation comes from political instability, poor infrastructure, and natural disasters like droughts10. Countries like Zimbabwe, Sudan, and Ethiopia face severe inflation and economic issues due to poor management and conflict.
Food prices have soared in Africa, with maize and wheat prices up by 12% and 14% respectively, pushing up the cereal price index by 10%10. Countries like Venezuela, Lebanon, and Zimbabwe saw huge food price hikes, with real food inflation highest in Zimbabwe, Egypt, and Lebanon10.
Europe: Mixed Fortunes and Policy Responses
Europe, unlike Africa, generally has lower inflation rates10. Yet, there are big differences across the region. The UK and Italy have seen high inflation, while Germany and France have kept it under control10.
European central banks and governments have used policies like raising interest rates and fiscal measures to fight inflation11. These efforts have shown mixed results, showing how complex the inflation issue is in Europe.

“Geoeconomic weaponization may result in inefficient production and rising prices.”11
Inflation and Global Supply Chain Disruptions
Impact of the Russia-Ukraine War on Food and Energy Prices
The Russia-Ukraine war has greatly affected global inflation. It has pushed up prices of key goods like oil, gas, and food. These items are major exports from both countries12. The conflict has made production and trade in these goods harder, causing prices to rise worldwide12.
This has led to higher costs for many things, like getting goods from one place to another, making food and other essential items more expensive12.
The Global Supply Chain Pressure Index hit a record high in April 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic. It even got worse by December 202112. But by October 2023, it was back to a normal level, showing some relief12.
Studies say supply chain issues were a big reason for inflation in the U.S. from 2021 to 202212. After the Great East Japan Earthquake in 2011, Japan’s economy grew less, affecting many businesses through supply chains12.
Companies started using just-in-time supply chains in the 1970s to save money. But this made them more vulnerable to problems like the pandemic12. On the other hand, having diverse supply chains can cut down on economic losses from big events by a lot12.
The pharmaceutical and medical products industry has faced more shortages because of limited supply chain diversity. This has led to more shortages of important items12. Trading with more countries can make supply chains more resilient to economic shocks12.
The Global Supply Chain Pressure Index went way up by the end of 2021 because of COVID-1913. It showed a strong link with inflation, especially during the pandemic13.
A big shock in the Global Supply Chain Pressure Index could raise inflation by about 0.5 percentage points. Goods prices could go up by 1.5 percentage points more than before13. It also could make unemployment go up by 0.7 percentage points13.
A shortage of chips in late 2020 led to a lack of many products, including cars. This made inflation go up because of higher car prices14. The U.S. has a big shortage of workers, with about 1.2 job openings for every worker14. The economy grew by 2.5% in 2023, but slowed down to 1.3% in the first quarter of 202414.
Central Bank Policies and Inflation-Fighting Strategies
Central banks and governments use tools like raising interest rates and adjusting the money supply to fight inflation15. The U.S. Federal Reserve, for example, raised interest rates by 4.25 points in 2022 to tackle high inflation15. Yet, balancing inflation control with economic growth is a tough task.
How well these measures work varies by country’s economic conditions and policies15. In the U.S., growth is expected to slow down to 0.5% in 2023, while Germany and the U.K. might see declines15. Central banks, like the Bank of England, are debating how fast to raise rates to fight inflation. This is a big concern in Europe due to the impact on growth.
The European Central Bank focuses a lot on inflation, thanks to Germany’s influence, and is cautious about raising rates15. The U.K. government plans to cut energy subsidies, raise taxes, and cut public spending to fight inflation, which is not popular with the public15.
Central banks and policymakers face a tough challenge as they try to manage inflation without hurting economic growth and stability15. The future of inflation is uncertain, with worries of stagflation, high inflation and slow growth, becoming a real threat15.
Central bank policies and government strategies are key to fighting inflation, but their success depends on many factors15. As we face this inflation challenge, policymakers must stay alert and flexible. They need to find the right balance between controlling prices and promoting economic growth.
Ripple Effects: How High Inflation Impacts Economies and Societies
High inflation does more than just raise prices. It eats away at what money can buy, leading to lower living standards16. People find it hard to get by, making tough choices on everyday items. This affects the economy by reducing spending and slowing growth.
Erosion of Purchasing Power and Living Standards
High inflation makes keeping up with life costs harder. As prices go up, what money can buy goes down. People spend less and make hard money choices16. This means living standards drop as they can’t afford basic things like food, homes, and healthcare.
Investment and Trade Implications
Inflation hurts investment and trade too. It makes investors wary, leading them to avoid long-term plans16. This slows down growth by reducing innovation and jobs. Also, it changes trade by making some products less competitive and imports pricier16.
High inflation’s effects spread wide, hitting people’s buying power and living standards. It also affects investments and trade. To tackle these issues, we need strong policies and a clear understanding of how inflation works with money and the economy16.
Potential Solutions and Economic Policies to Combat Inflation
Governments and central banks are working hard to fight high inflation. They use many policies and strategies to do this17. By cutting public spending by 1% of GDP since 1985, inflation has dropped by half a percentage point in advanced economies17. Also, high inflation can reduce public debt by 0.6% of GDP for countries with debt over 50% of GDP, for each point of inflation increase, lasting years.
One main way to fight inflation is by raising interest rates18. By August 2023, interest rates and Treasury yields were higher than inflation, showing this method works17. Cutting spending can also help, especially if done with policies to protect the vulnerable. This way, interest rates don’t have to go up as much to fight inflation.
17 Inflation can lower real incomes in countries that import a lot of commodities, as wages don’t keep up with prices17. In poor countries, the rise in food prices hits the poorest families hard, since food takes up a big part of their budget.
17 At first, inflation makes deficit-to-GDP ratios go down, but this effect doesn’t last as spending doesn’t keep up with the rising value of the economy’s output17. In countries with strong financial and credit markets, families with a negative net worth might have gained as inflation reduced the value of assets and debts.
To really tackle inflation, we need a mix of monetary, fiscal, and targeted policies1718.
| Policy Measure | Impact on Inflation |
|---|---|
| Raising Interest Rates | Reduces inflation by tightening monetary policy and discouraging borrowing and spending. |
| Adjusting Money Supply | Decreases the amount of money in circulation, which can help lower inflation. |
| Fiscal Policies (Tax Cuts, Government Spending) | Can either stimulate or dampen economic activity, depending on the specific policies implemented. |
| Coordinated Global Action | International cooperation and policy coordination can address the global nature of inflationary pressures. |
“Effectively addressing high inflation requires a comprehensive and coordinated approach that combines monetary, fiscal, and targeted policies to protect the most vulnerable segments of the population.”
Conclusion: Navigating the Global Inflationary Storm
The world is dealing with a big inflation problem in 2023. Many countries are seeing their highest inflation in decades19. This crisis comes from the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain issues, and the Russia-Ukraine war. Some countries are getting their inflation under control, but others are still facing high prices19.
To beat this inflation, we need a strong plan. This plan should come from central banks, governments, and the world working together20. It’s important for economies to be able to change and use good strategies. This will help keep the economy stable and prosperous.
The future of dealing with global inflation is not clear19. But, if everyone works together and focuses on long-term fixes, we can lessen the effects of inflation. This will help businesses, consumers, and communities worldwide.
FAQ
What are the countries with the worst inflation rates in the world in 2023?
The top countries with the highest inflation rates in 2023 are Zimbabwe, Venezuela, and Sudan. Zimbabwe leads with 284.94%, followed by Venezuela at 210%, and Sudan at 154.91%.
What is the definition of inflation and why does it matter?
Inflation means prices go up over time. It’s a key economic indicator that affects how much money you can buy. A little inflation can help the economy grow. But too much can lower what you can buy, cause uncertainty, and raise interest rates.
What are the causes of the high inflation rates in Zimbabwe and Venezuela?
Zimbabwe’s high inflation comes from a long economic crisis and international sanctions. Venezuela’s inflation is due to economic collapse, corruption, and US sanctions.
What are the key drivers and factors contributing to the worst inflation in the world in 2023?
Many things are causing high inflation in 2023. The COVID-19 pandemic, supply chain issues, and the Russia-Ukraine war are main factors. These events have led to price hikes and supply shortages. Governments’ efforts to help their economies during the pandemic have also added to inflation.
Which regions are experiencing the highest inflation rates, and what are the contributing factors?
Africa is seeing high inflation due to political issues, poor infrastructure, and natural disasters. In Europe, inflation is lower but varies by country. This depends on their economic policies.
How has the Russia-Ukraine war impacted global inflation?
The war has pushed up global inflation by affecting the supply and prices of important goods. Russia and Ukraine are big suppliers of oil, gas, and food. The conflict has made these goods more expensive, affecting many industries.
What tools are governments and central banks using to combat high inflation, and how effective are these measures?
Governments and central banks are using tools like higher interest rates and changing money supply to fight inflation. But controlling inflation without hurting growth is hard. The success of these efforts depends on each country’s economic situation.
How does high inflation impact economies and societies?
High inflation lowers what money can buy, making life harder for people. It can reduce living standards and cause financial stress. It also makes investing uncertain, affecting trade and the economy.
Source Links
- Inflation by Country 2023 – Wisevoter – https://wisevoter.com/country-rankings/inflation-by-country/
- List of Countries by Inflation Rate 2023 – https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/inflation-rate-by-country/
- What Is Inflation? How Rising Prices Can Erode Your Purchasing Power | Bankrate – https://www.bankrate.com/banking/federal-reserve/what-is-inflation/
- What is Inflation and Why Does it Matter? – https://www.pgpf.org/budget-basics/what-is-inflation-and-why-does-it-matter
- Which countries have the highest level of inflation in 2023? – https://www.investmentmonitor.ai/insights/which-countries-have-the-highest-level-of-inflation-in-2023/
- 20 Countries With The Highest Inflation in 2023 – https://finance.yahoo.com/news/20-countries-highest-inflation-2023-144808256.html
- 2021–2023 inflation surge – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/2021–2023_inflation_surge
- Inflation in 2023: Causes, Progress, and Solutions – https://oversight.house.gov/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/inflation_testimony_mkonczal_current.pdf
- World’s Highest And Lowest Inflation Rates 2024 – Global Finance Magazine – https://gfmag.com/data/economic-data/worlds-highest-lowest-inflation-rates/
- PDF – https://thedocs.worldbank.org/en/doc/40ebbf38f5a6b68bfc11e5273e1405d4-0090012022/related/Food-Security-Update-XC-July-27-2023.pdf
- Global Risks Report 2023 | World Economic Forum – https://www.weforum.org/publications/global-risks-report-2023/digest/
- Issue Brief: Supply Chain Resilience | CEA | The White House – https://www.whitehouse.gov/cea/written-materials/2023/11/30/issue-brief-supply-chain-resilience/
- Global Supply Chain Pressures and U.S. Inflation – San Francisco Fed – https://www.frbsf.org/research-and-insights/publications/economic-letter/2023/06/global-supply-chain-pressures-and-us-inflation
- How Do Supply Chain Disruptions Contribute to Inflation? | U.S. Bank – https://www.usbank.com/investing/financial-perspectives/market-news/supply-chain-issues-contribution-to-inflation.html
- Global economy 2023: Why central banks face an epic battle against inflation amid political obstacles – https://theconversation.com/global-economy-2023-why-central-banks-face-an-epic-battle-against-inflation-amid-political-obstacles-197088
- The Inflation Outlook: Four Scenarios for 2023-2025 – https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/operations/articles/the-inflation-outlook-four-futures-for-us-inflation.html
- Fiscal Policy Can Help Tame Inflation and Protect the Most Vulnerable – https://www.imf.org/en/Blogs/Articles/2023/04/03/fiscal-policy-can-help-tame-inflation-and-protect-the-most-vulnerable
- Is Inflation on the Way Out or Here to Stay? – https://www.stlouisfed.org/on-the-economy/2023/oct/inflation-way-out-here-stay
- What is inflation? – https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/mckinsey-explainers/what-is-inflation
- Looking ahead: Global economic outlook for 2023 – https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/economy/spotlight/global-economic-outlook-2023.html