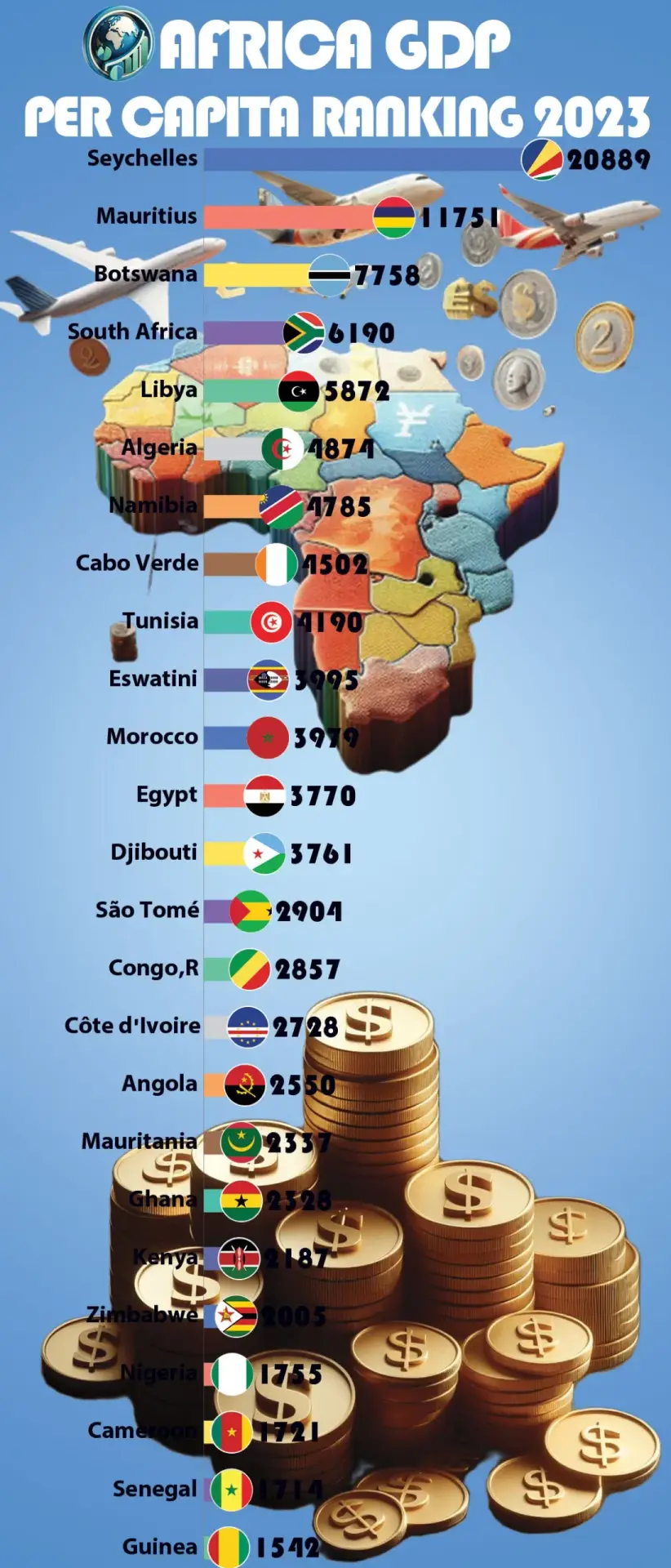
The Seychelles is the richest African country by GDP per capita, with a GDP per capita of $14,653 in 20211. Mauritius and Gabon are close behind with GDP per capita of $9,106 and $8,635 respectively1. South Africa, Botswana, Libya, Namibia, Eswatini, and Tunisia also rank high1.
list of richest countries in africa 2023
| Flag | Country | GDP per capita (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 🇸🇨 | Seychelles | 20,889.545 |
| 🇲🇺 | Mauritius | 11,751.506 |
| 🇧🇼 | Botswana | 7,758.371 |
| 🇿🇦 | South Africa | 6,190.742 |
| 🇱🇾 | Libya | 5,872.222 |
| 🇩🇿 | Algeria | 4,874.706 |
| 🇳🇦 | Namibia | 4,785.679 |
| 🇨🇻 | Cabo Verde | 4,502.784 |
| 🇹🇳 | Tunisia | 4,190.603 |
| 🇸🇿 | Eswatini | 3,995.029 |
| 🇲🇦 | Morocco | 3,979.871 |
| 🇪🇬 | Egypt | 3,770.133 |
| 🇩🇯 | Djibouti | 3,761.241 |
| 🇸🇹 | São Tomé and Príncipe | 2,904.715 |
| 🇨🇬 | Congo, Republic of | 2,857.614 |
| 🇨🇮 | Côte d’Ivoire | 2,728.079 |
| 🇦🇴 | Angola | 2,550.001 |
| 🇲🇷 | Mauritania | 2,337.914 |
| 🇬🇭 | Ghana | 2,328.970 |
| 🇰🇪 | Kenya | 2,187.648 |
| 🇿🇼 | Zimbabwe | 2,005.875 |
| 🇳🇬 | Nigeria | 1,755.326 |
| 🇨🇲 | Cameroon | 1,721.954 |
| 🇸🇳 | Senegal | 1,714.653 |
| 🇬🇳 | Guinea | 1,542.757 |
| 🇪🇹 | Ethiopia | 1,473.360 |
| 🇧🇯 | Benin | 1,449.112 |
| 🇿🇲 | Zambia | 1,435.890 |
| 🇰🇲 | Comoros | 1,377.022 |
| 🇹🇿 | Tanzania | 1,326.634 |
| 🇺🇬 | Uganda | 1,163.034 |
| 🇱🇸 | Lesotho | 1,110.179 |
| 🇷🇼 | Rwanda | 1,031.692 |
| 🇬🇼 | Guinea-Bissau | 1,028.223 |
| 🇹🇬 | Togo | 1,004.466 |
| 🇲🇱 | Mali | 912.643 |
| 🇬🇲 | Gambia, The | 903.293 |
| 🇧🇫 | Burkina Faso | 888.029 |
| 🇱🇷 | Liberia | 800.213 |
| 🇸🇴 | Somalia | 717.406 |
| 🇹🇩 | Chad | 702.845 |
| 🇨🇩 | Congo, Dem. Rep. of the | 675.477 |
| 🇲🇿 | Mozambique | 647.135 |
| 🇳🇪 | Niger | 630.800 |
| 🇲🇼 | Malawi | 579.701 |
| 🇸🇩 | Sudan | 533.845 |
| 🇲🇬 | Madagascar | 529.560 |
| 🇸🇸 | South Sudan, Republic of | 417.438 |
| 🇸🇱 | Sierra Leone | 414.962 |
| 🇧🇮 | Burundi | 245.811 |
SOURCE International Monetary Fund (IMF)
This data shows that GDP per capita varies a lot across Africa. Some countries like Seychelles and Mauritius are very prosperous. Others face big challenges with poverty.
Key Takeaways
- Seychelles is the richest African country by GDP per capita, with a value of $14,653.
- Mauritius and Gabon are the second and third richest African countries by GDP per capita.
- GDP per capita varies greatly across Africa, indicating economic disparities within the continent.
- Some African nations like Seychelles and Mauritius have achieved high levels of prosperity, while others struggle with widespread poverty.
- Understanding GDP per capita is crucial for measuring a country’s economic performance and standard of living.
Introduction to GDP Per Capita in African Countries
Africa GDP per Capita Ranking 2023
Source: Image data (2023)
GDP per capita shows how wealthy a country is and how well its people live2. It’s found by dividing a country’s total GDP by its people. This tells us about the average income and how productive the country is2. For African countries, it’s a key way to see how rich and developed they are compared to each other.
What is GDP Per Capita?
GDP per capita is a key economic number that shows a country’s total output divided by its people3. It’s like a quick look at the average income and wealth of its people3. Experts and investors use it to understand a country’s economy and its growth potential.
Importance of GDP Per Capita in Measuring a Country’s Wealth
GDP per capita is important because it shows how well a country does economically and how happy its people are2. It helps us see how developed a country is by looking at its average income and living standard2. For African countries, it’s a key way to see who is doing the best economically.
This number gives us a full picture of a country’s economy, letting us compare countries and see how they’re doing over time2. It’s a big help for leaders, economists, and groups like the World Bank to make plans and check if their policies are working2.
Looking at GDP per capita gives us important info on African countries. We learn about their ability to produce, how much people earn, and their growth potential2. This info is key for making smart decisions and planning investments in Africa234.
Seychelles: Africa’s Richest Country by GDP Per Capita
The Seychelles leads Africa with a GDP per capita of $21,580 in 20235. Its economy heavily relies on tourism, making it prone to global issues5. The IMF data shows Seychelles is the wealthiest African nation, thanks to its strong service sector and resource management.
Seychelles’ GDP Per Capita and Economic Overview
Seychelles boasts the highest GDP per capita in Africa at $15.8 billion in 20225. Tourism makes up 31% of its GDP and 41% of exports, making it sensitive to global events5. The economy grew by 8.9% in 2022 and is expected to slow down to 3.3% in 20235. By the end of 2023, inflation was -2.7%, set to rise to 3.4% in 20245. Public debt fell to 60.1% of GDP in 20235.
Factors Contributing to Seychelles’ High GDP Per Capita
Seychelles is the wealthiest African nation with a GDP per capita of $39,6626. It outpaces countries like Madagascar ($1,500), Somalia ($1,400), and Afghanistan ($1,500)7. Seychelles ranks 80th globally in GDP per capita, surpassing countries like Liechtenstein ($139,100), Luxembourg ($117,700), and Monaco ($115,700)7. Its prosperity stems from a booming tourism sector, wise natural resource management, and a robust fishing industry.
Non-performing loans in the banking sector rose to 8.1% by December 20235. The current account deficit shrank to an estimated 5.6% of GDP in 20235. Foreign direct investments in Seychelles were 13.8% of GDP in 20235. Foreign exchange reserves grew to $681 million in 2023, covering 3.8 months of imports5.
“Seychelles’ high GDP per capita reflects its successful diversification into a service-based economy, particularly tourism, as well as its effective management of natural resources and fishing industry.”
Mauritius: Second Richest African Country by GDP Per Capita
Mauritius is an island nation off Africa’s southeast coast. It’s the second richest African country by GDP per capita8. With a GDP per capita of $9,640 in 2021, it has a diverse and stable economy. This makes it a top example of economic growth in the area8.
The country’s economy is strong in tourism, financial services, and manufacturing. These sectors help make its standard of living higher than many other African countries9.
In 2022, Mauritius’ GDP was estimated at $11.263 billion (nominal) and $31.720 billion (PPP)9. The GDP per capita was $8,892 (nominal) and $25,043 (PPP)9. The economy is expected to grow by 6.2% in 2022, driven by tourism and other sectors10.
However, Mauritius faces challenges like a high trade deficit and inflation. The trade deficit was 35.1% of GDP in 2022, and inflation is expected to be around 10.4%10. Yet, its efforts to diversify the economy and strengthen its financial sector keep it among the top African countries by GDP per capita8.
Mauritius also excels in social and human development. It has a Human Development Index of 0.802 in 2021 and a poverty rate of just 8% as of 20069. The unemployment rate is 8.6% as of 2020, with a labor force participation rate of 65.3%9.
In conclusion, Mauritius is known as the second richest African country by GDP per capita. Its success comes from wise economic policies, a diverse economy, and a focus on sustainable development. Despite challenges like inflation and trade deficits, its strong economy and resilience make it a model for other African nations8910.,,
Libya: A Wealthy Nation Driven by Oil Revenue
Libya is the third richest African country by GDP per capita, with a GDP per capita of $6,987 in 202411. But, its economy has been hit hard by political issues and conflict. These problems have greatly affected its economic growth and development.
Libya’s GDP Per Capita and Economic Landscape
In 2024, Libya’s GDP (PPP) is expected to be $183.39 billion, ranking 79th globally11. Its nominal GDP is set to be $48.22 billion, making it 93rd in the world11. The country’s population is expected to hit 7,361,263 in 2024, placing it 106th globally11.
Libya is seen as one of Africa’s upper middle-income countries12. Its Human Development Index (HDI) score is 0.746 as of 2022. This puts it in the high HDI category and ranks it 92nd globally11.
Impact of Oil on Libya’s Economy
Oil revenues are a big part of Libya’s economy, boosting its GDP per capita13. Hydrocarbons account for about 95% of Libya’s exports and government income13. Libya has the 10th-largest proven oil reserves in the world11.
After the Arab Spring in 2011, Libya faced political instability. This led to delays in national elections, originally set for December 202112. This instability hurt the economy, causing a 30% drop in nominal GDP in 2020 due to an oil blockade and lower oil prices13.
But, Libya has seen budget surpluses in 2021 and 2022. This was thanks to a rise in oil prices and production13. In 2022, the government spent about US$7 billion on the National Oil Corporation (NOC) for development, supporting the oil sector13.
Libya’s economy has its challenges, like high inflation, a big public sector, and a large informal sector13. Yet, Libya’s gross official reserves were US$82 billion at the end of 2022. This amount covers more than 4 years of imports, showing the country’s strong financial health13.
“Libya’s economy is heavily dependent on oil revenues, which have significantly contributed to its high GDP per capita.”
richest african countries by gdp per capita
Africa is a diverse continent with different economic conditions and development levels. Some African nations have improved their citizens’ standard of living. Others still face big challenges. GDP per capita is a way to measure a country’s wealth, showing the average income per person1.
Top African Countries by GDP Per Capita
The World Bank lists the top African countries by GDP per capita. These are Seychelles, Mauritius, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, South Africa, Botswana, Libya, Namibia, Eswatini, and Tunisia1. Seychelles leads with a GDP per capita of $14,5401. Mauritius is second with $9,1061. Libya ranks third with $8,7001. South Africa is fifth with $7,0551. Botswana is sixth with $6,8051.
Other countries with high GDP per capita include Cameroon ($4,660), Republic of the Congo ($5,550), Nigeria ($6,150), Kenya ($6,580), Ghana ($6,910), Côte d’Ivoire ($6,960), Djibouti ($6,990), Angola ($7,080), Mauritania ($7,540), Cabo Verde ($9,910), Morocco ($10,410), Namibia ($11,600), and Eswatini ($11,860)14.
Challenges Faced by Economies in Africa
Even though some countries have high GDP per capita, Africa faces big challenges. These include poverty, political instability, and limited access to resources and technology1. Many African economies struggle with inequality, relying too much on natural resources, and the COVID-19 pandemic’s effects1.
Seychelles has the highest GDP per capita in Africa, at $43,151. Mauritius is second with $32,094, Libya third with $26,456, Botswana fourth with $20,097, and Gabon fifth with $19,45215. Yet, even the wealthiest countries face challenges. For example, Botswana is trying to diversify its economy. Algeria depends too much on hydrocarbon production15.
Despite progress in some countries, Africa still faces many challenges. Overcoming these will be key to improving living standards and creating a prosperous future for all Africans11415.
South Africa: A Powerhouse with Economic Potential
South Africa is the second-biggest economy in Africa, showing great economic potential despite challenges. It has a GDP per capita of $5,975 (nominal, 2024 est.) and $16,424 (PPP, 2024 est.)16. This makes it the sixth richest African nation by this key measure. The country’s economy is strong in mining, manufacturing, and financial services, making it a key player in the region16.
South Africa’s GDP Per Capita and Economic Profile
South Africa’s GDP (PPP) shows its economic strength and potential in the region17. With a GDP of $373.23 billion (nominal, 2024 est.) and $1.026 trillion (PPP, 2024 est.)16, it’s expected to grow slowly. The growth rate is 0.6% in 2023, 0.9% in 2024, and 1.2% in 202516. But, it also has big challenges like a 32.1% unemployment rate and 44% for youth (15 to 24-year-olds; Q4 2023 est.)16.
The inflation rate of 4.9% in 202416 is a worry, affecting consumers and the economy. South Africa’s public debt, expected to hit 75.8% of GDP in 202416, shows the government’s financial burden. This could affect the country’s fiscal health and stability17.
Despite challenges, South Africa is still a top choice for foreign investment, with an FDI stock of $156.8 billion (as of 31 December 2017 est.)16. Its strategic location, diverse industries, and skilled workers attract international investment, showing its economic potential17.

As Africa’s second-largest economy, South Africa is key to the continent’s economic scene. It faces many challenges but still has a lot of potential. Its diverse industries, strategic location, and efforts to tackle unemployment, inequality, and fiscal stability are driving its growth18.
“South Africa’s economy is a complex, multi-faceted powerhouse, with both immense potential and daunting challenges. Its journey towards sustainable growth and prosperity requires a delicate balance of policy reforms, investment, and a commitment to inclusive development.”
Gabon: A Resource-Rich Nation with High GDP Per Capita
Gabon is a Central African country known as the fourth richest by GDP per capita. In 2021, its GDP per capita was $8,63519. This shows how its oil and natural gas have boosted its economy19.
The economy of Gabon relies a lot on these resources. They make up a big part of its GDP and exports19. The main industries are oil and gas, manganese mining, and gold mining19. Gabon also has a strong manufacturing sector, making chemicals, ships, food, textiles, and cement19.
But, Gabon’s economy is at risk because it depends too much on natural resource prices19. The government is trying to make the economy more diverse20. It aims to grow mining, timber, and agriculture as oil production drops from 202521.
| Key Economic Indicators | Value |
|---|---|
| GDP (nominal, 2018) | $16.875 billion19 |
| GDP (PPP, 2018) | $37.840 billion19 |
| GDP per capita (nominal, 2023 est.) | $9,42019 |
| GDP per capita (PPP, 2023 est.) | $19,83419 |
| Population below poverty line | 33.4% (2017)19 |
| Unemployment | 27% (2012 est.)19 |
Even with its rich economy, Gabon has issues with income inequality and improving people’s lives20. The Gini coefficient shows a medium level of income inequality in 201720. Gabon ranks 123rd on the Human Development Index (HDI) in 2022, highlighting the need for better education, healthcare, and social welfare20.
As Gabon deals with its challenges, its economy and high GDP per capita keep it important in Africa’s economy20. Diversifying its economy and reducing income inequality are key to its future and people’s well-being201921.
Botswana: A Stable and Prosperous African Economy
Botswana is a top example of economic growth and stability in Africa. It has a GDP per capita of $6,805 in 2021, making it the sixth richest in Africa22. The country’s success comes from its diamond mining, tourism, and financial services. Despite high unemployment and inequality, Botswana keeps its economy stable and prosperous, making it a promising nation.
Botswana’s GDP Per Capita and Economic Highlights
Botswana’s economy has grown steadily, with a GDP of $21.90 billion expected in 202423. Its GDP per capita is $7,859 in nominal terms and $20,158 in PPP for 2024, ranking 87th and 83rd globally23. This wealth is shown in its high Human Development Index score of 0.708, classified as “high” in 202223.
The diamond industry is a big part of Botswana’s growth, making up a third of its GDP and half of public spending24. The country is also working to diversify its economy. The services sector makes up 70.6% of GDP, followed by industry at 27.5%, and agriculture at 1.8%23.
Despite its success, Botswana faces challenges like high unemployment, with a rate of 25.9% as of 2023Q322. Income inequality is also a concern, with a Gini index of 53.322. Yet, Botswana’s good governance, low inflation, and stable currency help it stand out in Africa.

“Botswana has long been considered one of the most stable, prosperous, and well-governed countries in Africa. Its economic success is a testament to its commitment to sound policies, prudent management of its natural resources, and a focus on human capital development.”
Looking forward, Botswana’s growth is expected to slow to 3.3% in 2023, after 5.8% in 202222. The country’s fiscal deficit is set to reach 3.4% of GDP in 2023, and public debt will likely increase to 25.0% of GDP22. Despite these issues, Botswana remains a beacon of economic stability and prosperity in Africa, with a promising future222324.
Equatorial Guinea: An Oil-Dependent Economy
Equatorial Guinea is a small country in Central Africa that’s the seventh richest by GDP per capita25. It has a population of about 1.5 million people25. The country’s economy thrives on its oil and gas, making it very wealthy.
Equatorial Guinea’s GDP Per Capita and Reliance on Oil
In 2021, Equatorial Guinea’s GDP per capita was $7,50725. This makes it one of Africa’s wealthiest countries. The country’s oil and gas reserves, found in the mid-1990s26, have driven its economic growth. Now, oil and gas make up a big part of its economy26.
But, relying too much on oil and gas makes Equatorial Guinea’s economy unstable26. The country is trying to grow other sectors and spread wealth more evenly. Yet, two-thirds of people lived in poverty by 202027.
Equatorial Guinea is working on economic reforms and new projects. In 2021, it passed an anti-corruption law for better transparency25. It also joined an IMF program to manage debt and improve finances25. The goal is to grow sectors like digital, energy, and tourism25.
But, the country imports most of its food, which has led to high prices and inflation25. Global issues and the Ukraine war have made things worse.
Even with challenges, Equatorial Guinea is important in Africa’s economy. Its oil and gas are key to its growth27. The country aims to diversify and grow in a way that’s good for everyone262527.
Conclusion
The analysis of GDP per capita shows big economic differences across Africa. A few countries like Seychelles, Mauritius, and Gabon are doing well. But, many face poverty, political issues, and lack of economic variety28.
Africa’s economy is set to hit $2.6 trillion by 202028, with spending by 128 million households reaching $1.4 trillion28. Yet, 10 of the world’s most unequal countries are here, with South Africa and others leading the list28.
Fixing these issues and promoting growth is key to better living standards and less inequality in Africa29. The region’s growth is expected to rise to 3.7 percent in 2024 and 4.3 percent in 202529, making it the second-fastest growing area29. But, there’s a huge financing gap of about US$402 billion a year until 2030 for key Sustainable Development Goals29.
To reach their full potential, African countries should focus on diversifying their economies, improving governance, and investing in people and infrastructure28. They have a lot going for them, like natural resources, a young population, and a spirit of entrepreneurship. But, they need to work hard and together to beat inequality and instability.
FAQ
What is the richest African country by GDP per capita?
The Seychelles is the richest African country by GDP per capita. It had a GDP per capita of ,653 in 2021, according to the World Bank.
Which countries follow Seychelles in terms of GDP per capita in Africa?
Mauritius and Gabon are close behind with GDP per capita of ,106 and ,635 respectively. South Africa, Botswana, Libya, Namibia, Eswatini, and Tunisia also rank high.
What is the significance of GDP per capita in measuring a country’s wealth and prosperity?
GDP per capita is a key metric for comparing wealth and living standards across countries. It shows a nation’s productive capacity and income levels. This makes it a vital indicator of economic development and prosperity.
What are the key factors that contribute to Seychelles’ high GDP per capita?
Seychelles’ high GDP per capita comes from its strong service sector, especially tourism. It also benefits from effective management of natural resources and the fishing industry.
How does Mauritius’ economy contribute to its high GDP per capita?
Mauritius has a diverse and stable economy. It includes tourism, financial services, and manufacturing. These sectors help boost its standard of living and economic development.
What is the role of natural resources in shaping Libya’s GDP per capita?
Libya’s economy relies heavily on oil, which boosts its GDP per capita. Yet, political instability and conflict have greatly affected its economic growth and development.
What are the major challenges facing African economies in terms of economic development and prosperity?
Africa faces big challenges like poverty, political instability, and limited resources and technology. Many economies struggle with inequality, relying too much on natural resources, and the COVID-19 pandemic’s effects.
How does South Africa’s diverse economy contribute to its GDP per capita?
South Africa, the second-largest economy in Africa, has a varied economy. It excels in mining, manufacturing, and financial services. But, it also deals with high unemployment, inequality, and COVID-19’s economic impact.
What is the role of natural resources in Gabon’s high GDP per capita?
Gabon’s economy is mostly based on oil and natural gas. These resources have raised its GDP per capita. But, its heavy reliance on these exports makes it prone to global price changes and the need for economic diversification.
What factors contribute to Botswana’s relatively high GDP per capita compared to other African countries?
Botswana’s economy is stable and prosperous, thanks to diamond mining, tourism, and a strong financial sector. It’s known for low inflation, a stable currency, and good governance, which boost its GDP per capita.
How does Equatorial Guinea’s dependence on oil and natural gas impact its GDP per capita?
Equatorial Guinea’s economy heavily relies on oil and gas. These have driven its high GDP per capita. But, this over-reliance makes it vulnerable to global energy price changes and challenges diversifying its economy and wealth distribution.
Source Links
- Richest African Countries 2024 – https://worldpopulationreview.com/country-rankings/richest-african-countries
- Economy of Africa – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_Africa
- List of African countries by GDP (nominal) – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_African_countries_by_GDP_(nominal)
- Overview – https://www.worldbank.org/en/region/afr/overview
- Overview – https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/seychelles/overview
- Seychelles ranks as Africa’s richest country, Global Finance Magazine reports – https://www.nation.sc/articles/20740/seychelles-ranks-as-africas-richest-country-global-finance-magazine-reports
- No title found – https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/field/real-gdp-per-capita/country-comparison
- 10 African countries with the highest GDP per capita, according to latest data – https://africa.businessinsider.com/local/markets/10-african-countries-with-the-highest-gdp-per-capita/3qtpzde
- Economy of Mauritius – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_Mauritius
- BTI 2024 Mauritius Country Report – https://bti-project.org/en/reports/country-report/MUS
- Libya – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Libya
- Libya – ISS African Futures – https://futures.issafrica.org/geographic/countries/libya/
- No title found – https://www.elibrary.imf.org/view/journals/002/2023/201/article-A001-en.xml
- 23 Richest Countries in Africa by GDP Per Capita in 2023 – https://finance.yahoo.com/news/23-richest-countries-africa-gdp-091427629.html
- The Richest Countries In Africa – https://www.worldatlas.com/gdp/the-richest-countries-in-africa.html
- Economy of South Africa – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_South_Africa
- Index of Economic Freedom: South Africa | The Heritage Foundation – https://www.heritage.org/index/pages/country-pages/south-africa
- Reimagining economic growth in Africa: Turning diversity into opportunity – https://www.mckinsey.com/mgi/our-research/reimagining-economic-growth-in-africa-turning-diversity-into-opportunity
- Economy of Gabon – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_Gabon
- Gabon – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gabon
- Overview – https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/gabon/overview
- Overview – https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/botswana/overview
- Economy of Botswana – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_Botswana
- Botswana: The Pragmatic Path to Prosperity – https://hir.harvard.edu/botswana-prosperity/
- Overview – https://www.worldbank.org/en/country/equatorialguinea/overview
- No title found – https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/about/archives/2022/countries/equatorial-guinea
- Economy of Equatorial Guinea – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Economy_of_Equatorial_Guinea
- Closing Africa’s wealth gap – https://www.un.org/africarenewal/magazine/december-2017-march-2018/closing-africa’s-wealth-gap
- African Economic Outlook 2024 – https://www.afdb.org/en/knowledge/publications/african-economic-outlook